Link Aggregation and LACP
A Link Aggregation Group (LAG) enables the grouping Ethernet interfaces to form a single link layer interface. LAGs are formed by connecting multiple ports in parallel between two devices. As more links are added between the two devices, bandwidth expands. Traffic is automatically load-balanced, and in a network failure scenario, there is link-level redundancy.
LACP is the protocol that defines how the group of interfaces operates. LACP enables dynamic LAG, allowing the exchange of information between the members of the LAG network, monitoring bundle endpoints, and adding or removing new or unused individual links.
A Link Aggregation Group (LAG) that does not have LACP enabled operates as a static LAG, where the interfaces do not communicate state information.
For a deeper look at LAG and LACP, see Aggregated Ethernet Interfaces.
How It Works
The LAG is created by defining a device interface as a bond. The bond interface is configured with a network-interface. Members of the bond are configured as ethernet device interfaces, and have the parent-bond setting defined as the bond device interface. bond members (the device interfaces) are not allowed to be configured with their own network-interfaces.
Requirements
LAG/LACP has the following requirements:
- LAG/LACP must be configured on the devices on each end of the link.
- A
bondmust have between 1 and 8 members. Members are device-interfaces that reference thebondinterface as theirparent-bond. - All members of the
bondmust be of the typeethernet. - All members of the
bondmust be the same speed and support full duplex.
Supported Platforms
All SSR hardware platforms (SSR100 Series and SSR1000 Series) are supported.
Configuring LAG and LACP
LACP is enabled by default on the bond device interface, and must be configured on each end of the link. The following device interface configuration shows a bond interface and lacp-enabled as true (default). The interfaces that are part of the LAG are configured as ethernet interfaces and the parent-bond is identified as the name of the bond interface.
Please note that after any changes to the LAG configuration, you must restart the 128T service.
Configuration Using the PCLI
- Create the LAG by configuring the
bonddevice-interface.- Name the interface
- Set the
typetobond lacp-enableis enabled by default
device-interface bond0
name bond0
type bond
bond-settings
lacp-enable true
exit
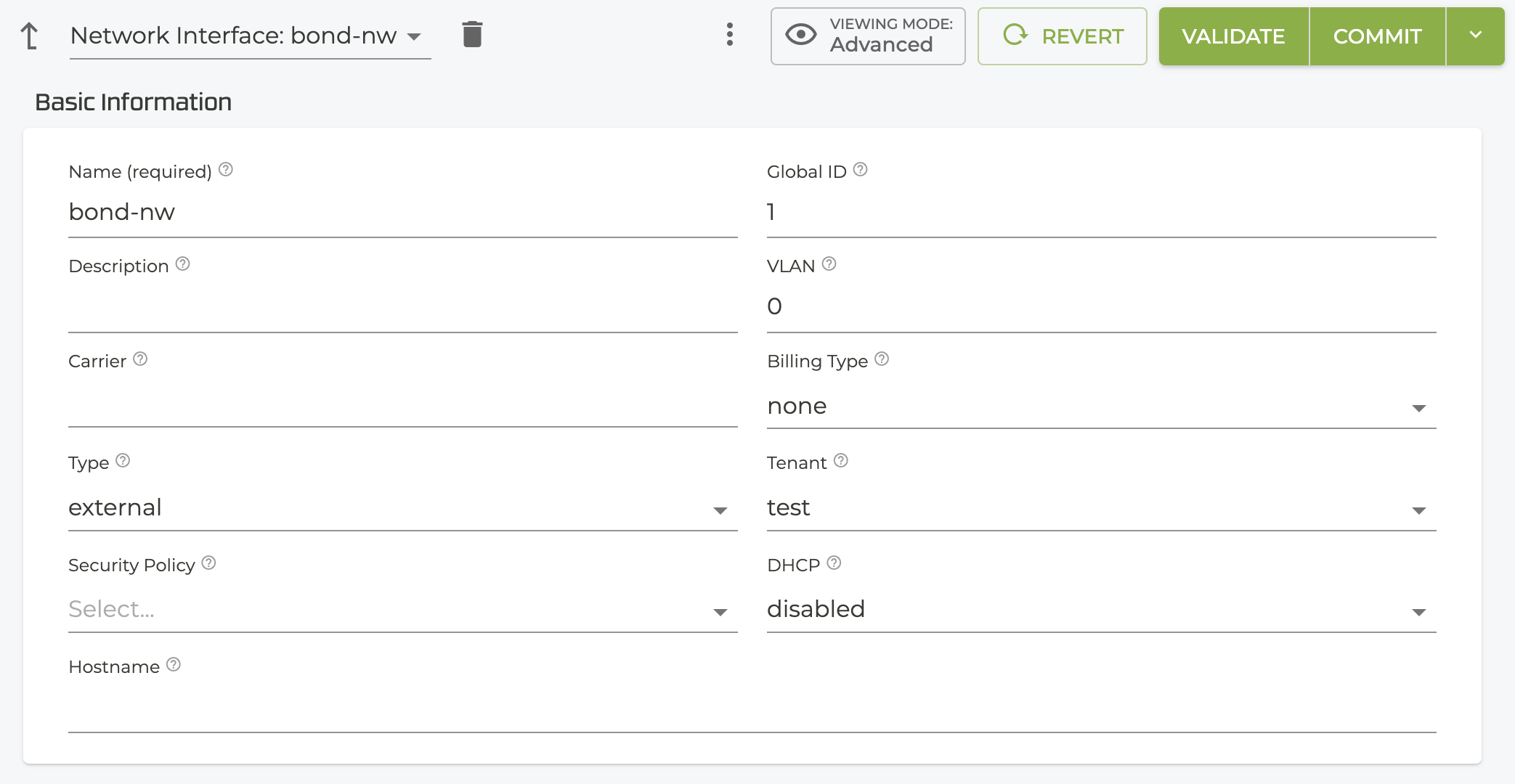
- Configure the network interface used by the LAG.
network-interface bond-nw
name bond-nw
global-id 1
tenant red
address 1.1.1.1
ip-address 1.1.1.1
prefix-length 24
gateway 1.1.1.100
exit
exit
exit
- Configure at least one device interface to be part of the LAG.
- Be sure to configure the
parent-bondwith the device name of thebondinterface. - The only configuration allowed on the bond-members are
pci-addressandparent-bond. All other settings must be configured on thebondinterface.
- Be sure to configure the
device-interface ge-0-1
name ge-0-1
type ethernet
pci-address 0000:04:00.0
parent-bond bond0
exit
device-interface ge-0-0
name ge-0-0
type ethernet
pci-address 0000:04:00.1
parent-bond bond0
exit
Configuration Using the GUI
These same settings are accessed from the GUI at the Authority > Router > Node > Device Interface level.
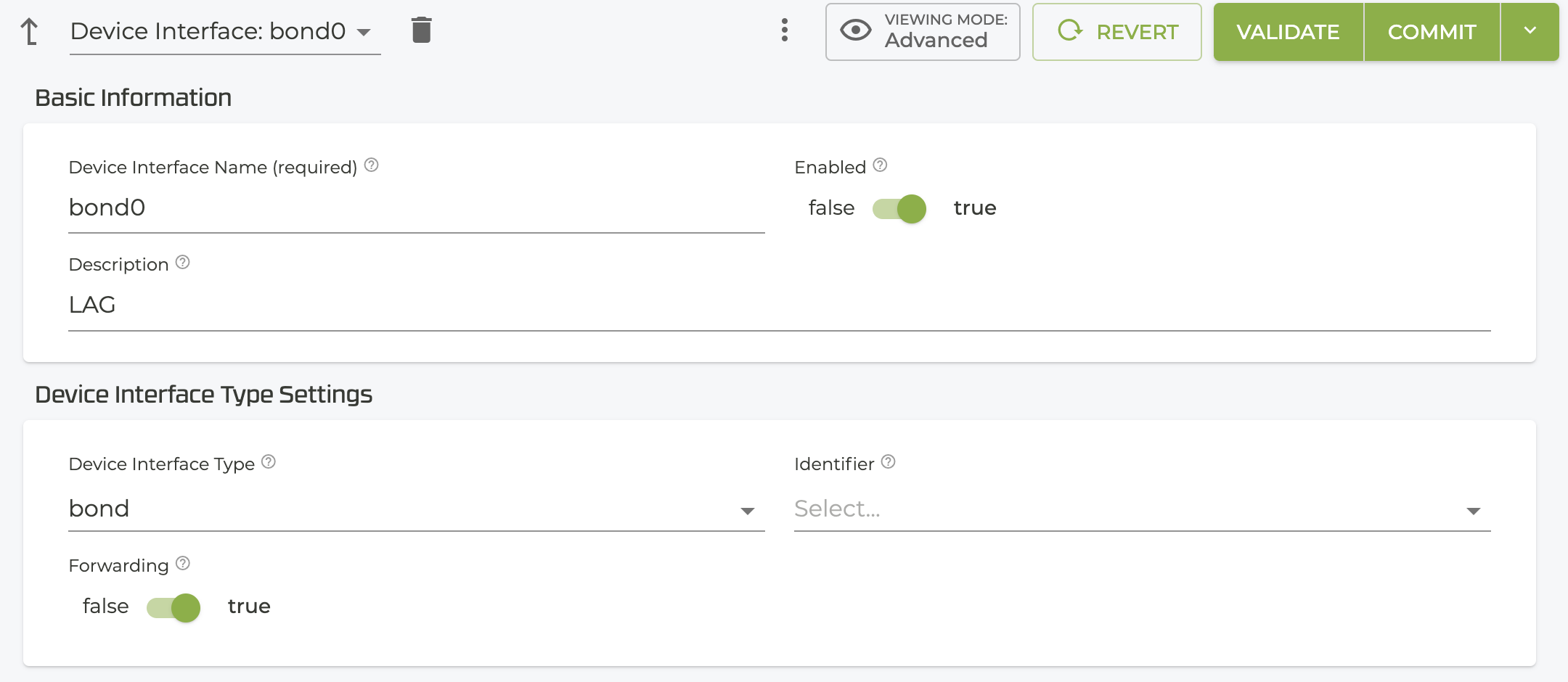
- Create the LAG by configuring the
bonddevice-interface.- Name the interface
- Set the
typetobond lacp-enableis enabled by default
- Configure the network interface used by the LAG.
- Configure at least one device interface to be part of the LAG.
- Be sure to configure the
parent-bondwith the device name of thebondinterface. - The only configuration allowed on the bond-members are
pci-addressandparent-bond. All other settings must be configured on thebondinterface.
- Be sure to configure the
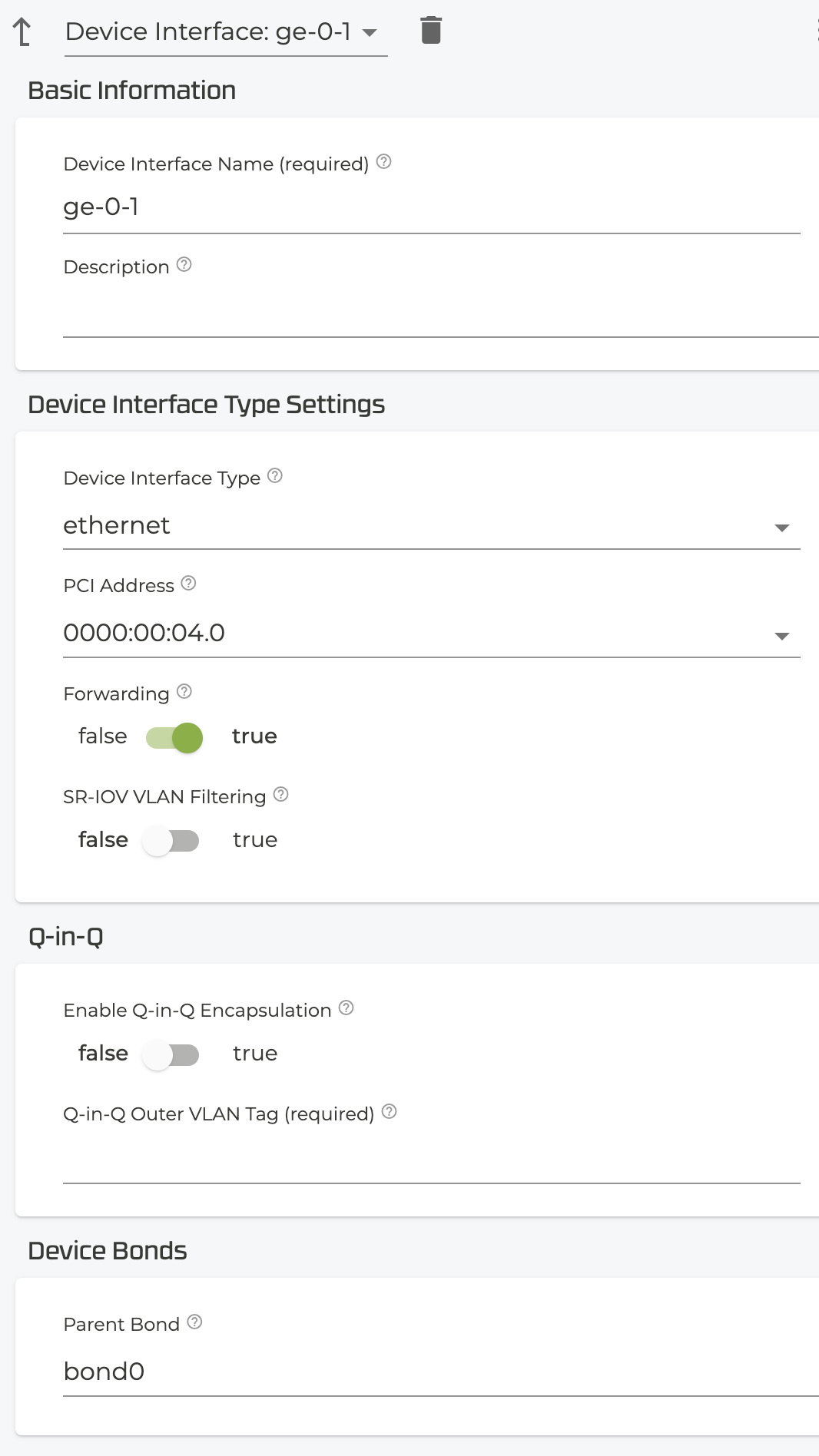
Force-up
When enabled, force-up allows one member of a bond interface to send and receive without the required LACP negotiation.
How It Works
force-up mode can only be enabled when LACP is enabled, and is disabled by default. When enabled, a bond interface that does not receive any LACP PDU's on any member interfaces over a configured time-out period enters the force-up mode. In this mode, one member of the bond is used as an active interface, sending and receiving without the required LACP negotiation.
Other interfaces continue to send and receive LACP PDUs, but will not accept or send any other frames. If at any time a member receives an LACP PDU, the bond’s force-up mode is cleared and it operates under normal LACP protocol.
Force-up is re-entrant; a bond interface can go into force-up mode, back to normal, and then into force-up mode again.
Example
An example use-case is a peer system that uses a PXE boot - a preboot environment where a device reaches out over the network to fetch a firmware/OS image - but is unable to support the LACP protocol to form the bond. Configuring force-up and time-out allows the SSR to bring the LACP interface up as an active interface without the required LACP negotiation, similar to a static-LAG. The peer system can then get the image, boot, and configure LACP. The SSR LACP bond will return to operating in LACP mode once it starts seeing LACP frames from the device.
Configuration
In this example, force-up is configured on the LACP enabled bond interface, with a timeout of 30 seconds.
config
authority
router red-1
node node_one
device-interface bond0
name bond0
description "Bonded Interface"
type bond
bond-settings
lacp-enabled true
force-up true
force-up-timeout 30
...
The force up mode is shown as part of the show device-interface output of the bond member information.
bond_members:
aggregator_port_id: 1
selection: SELECTED
actor_detail_info:
system_priority: 65535
system_mac_address: 90:ec:77:32:e3:f6
port_key: 17
port_priority: 255
port_number: 2
port_state: ACTIVE, TIMEOUT, AGGREGATION, DEFAULTED
partner_detail_info:
system_priority: 65535
system_mac_address: 00:00:00:00:00:00
port_key: 1
port_priority: 255
port_number: 0
port_state: ACTIVE
state_machine_flags: LACP_ENABLED, EXPIRED, FUP
Configuring LLDP
LLDP allows other devices in the network to discover the SSR. It is not required for LAG, but when enabled it provides information about the LAG interface in the network. It should be noted that when enabled as part of LAG, it is configured for the entirety of the bond, not on the individual interfaces within the group. For additional information about using the LLDP command, see lldp
device-interface bond0
name bond0
type bond
bond-settings
lacp-enable true
exit
lldp mode enabled
exit
exit
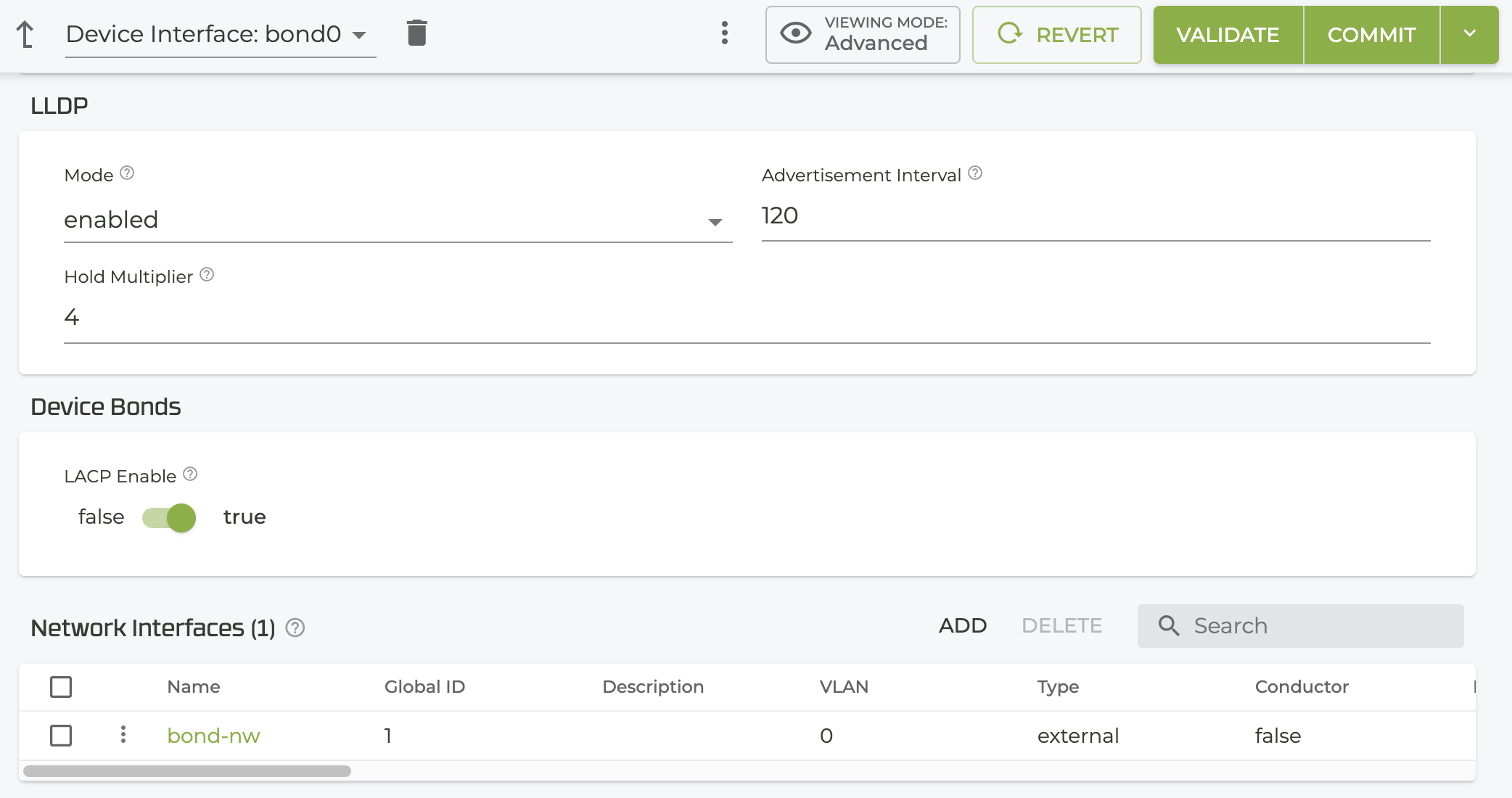
Show Commands
Use the show device-interface name <name> command to troubleshoot or view the status of the LAG/LACP interface.
admin@sn2028220232.router# show device-interface name bond0
Mon 2023-06-26 19:03:32 UTC
Retrieving device interface information...
=======================================================================================================
sn2028220232:bond0
=======================================================================================================
Type: bond
Forwarding: true
MAC Address: 90:ec:77:32:e3:f6
Admin Status: up
Operational Status: up
Provisional Status: up
Redundancy Status: non-redundant
Speed: 2 Gb/s
Duplex: full
in-octets: 73018210
in-unicast-pkts: 86729
in-errors: 0
out-octets: 5611232
out-unicast-pkts: 45281
out-errors: 0
Bond Information:
mode: LACP
device_port: 1
dpdk_port: 3
member_count: 2
active_members: 2
xmit_policy: LAYER34
bond_members:
aggregator_port_id: 1
selection: SELECTED
actor_detail_info:
system_priority: 65535
system_mac_address: 90:ec:77:32:e3:f6
port_key: 17
port_priority: 255
port_number: 2
port_state: ACTIVE, TIMEOUT, AGGREGATION, SYNCHRONIZATION, COLLECTING, DISTRIBUTING
partner_detail_info:
system_priority: 127
system_mac_address: 88:0a:a3:e6:5d:d4
port_key: 1
port_priority: 127
port_number: 1
port_state: ACTIVE, TIMEOUT, AGGREGATION, SYNCHRONIZATION, COLLECTING, DISTRIBUTING
aggregator_port_id: 1
selection: SELECTED
actor_detail_info:
system_priority: 65535
system_mac_address: 90:ec:77:32:e3:f5
port_key: 17
port_priority: 255
port_number: 1
port_state: ACTIVE, TIMEOUT, AGGREGATION, SYNCHRONIZATION, COLLECTING, DISTRIBUTING
partner_detail_info:
system_priority: 127
system_mac_address: 88:0a:a3:e6:5d:d4
port_key: 1
port_priority: 127
port_number: 2
port_state: ACTIVE, TIMEOUT, AGGREGATION, SYNCHRONIZATION, COLLECTING, DISTRIBUTING
Plugin Info: unavailable
Completed in 0.18 seconds