OTP Router Install Process
The simplest deployment of the One Touch Provisioning (OTP) solution is highly automated and leverages just two components, the Conductor and at least one SSR. For many customers, the SSR platform is ordered and delivered as a pre-integrated, off-the-shelf solution through the Juniper SSR partner network.
The OTP installation process produces a Router installed with SSR software set to factory defaults. Upon completing the OTP installation process, the default behavior is to provision the device with a DHCP client on the first ethernet port and DHCP server listening on all other ports. The user connects to the SSR via ethernet cable and uses the QuickStart file generated by the Conductor to finalize the SSR configuration. After performing the QuickStart operation, the SSR has connectivity to the conductor and downloads the latest configuration (if necessary) to begin operation.
This process assumes you have already created a bootable device using a USB. Instructions for downloading and creating a bootable device are available in Downloading an SSR ISO and Creating a Bootable USB.
Router installation can be performed using either the OTP process, or the Interactive Installation. You do not need to perform both. The steps in this section describes the OTP process.
The Conductor installation must be completed before installing a Session Smart Router or routers using the ISO. The same ISO is used for all installations.
QuickStart Provisioning
Basic configuration parameters are encoded within an encrypted file. For each node, a custom file can be exported from the Conductor and minimally contains the following configuration encoded parameters:
- WAN IP address, subnet mask and gateway
- Conductor IP address
- Asset ID
Before you Begin
Before beginning the Router installation, you must have a Conductor operationally deployed and reachable by the router.
For Common Criteria compliance, a dedicated, out-of-band network must be used to provide the management connection security between Conductor and Router instances. SSR software does not currently provide any evaluated security assurances for this link. This dedicated network interface must be privately routed, and must not be exposed publicly.
Installation
Connect the SSR to a Management Console
Ensure that you have an appropriate rollover cable available to connect to your computer. The SSR has a console port (CONSOLE) with an RJ-45 connector. Use the console port to connect the appliance to a management console or to a console server. The baud rate of the console port is 115200 bps.
- Connect the RJ45 rollover cable to the console port on the SSR device.
- Connect the other end of the cable to your computer.
- Insert your bootable USB with the new ISO image into the USB port of the SSR device.
- Connect the power input to the SSR device
- Power on the SSR.
Booting from the USB
Use the steps appropriate for your device to direct the device to boot from the USB for installation.
SSR100 Series Devices
- At the instruction in the terminal window:
Press ESC for boot menu, do so.

- From the boot menu, enter the device number corresponding to the USB, and press Enter.
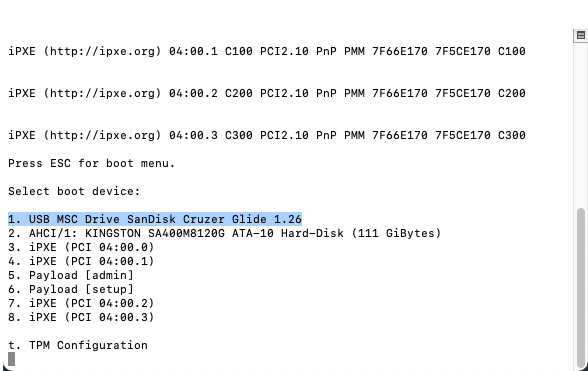
- When the USB installer boot menu is displayed, continue with the OTP Router Installation.
SSR1000 Series Devices
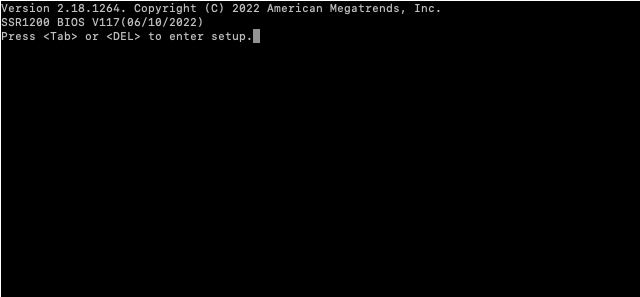
- At the instruction in the terminal window:
Press <Tab> or <DEL> to enter Setup, do so.
- When the Setup Utility window appears, use the left and right arrow keys to navigate to the
Save & Exittab.
- Use the up and down arrow keys to highlight the USB device in the the Boot Override list.
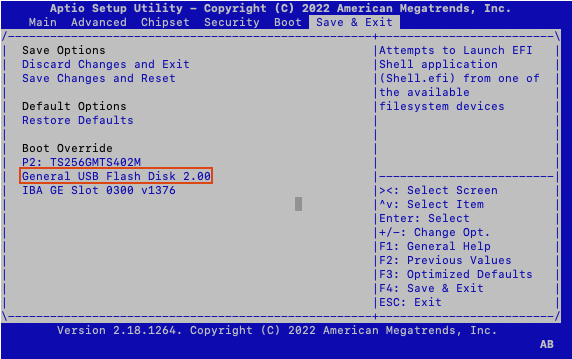
- Press Enter to confirm boot from the USB device.
- When the USB installer boot menu is displayed, continue with the OTP Router Installation.
OTP Router Installation
Upon boot, the following screen is displayed. The default selection is booting to the serial console (115200 baud). You must manually choose the installation process suited for your environment.
- Use the Up/Down keys to select the
OTP Install 128T Routing Software Serial Consoleoption. This is a supported installation option for Common Criteria. It uses/dev/ttyS0115200 baud as the serial console for interacting with the installer.
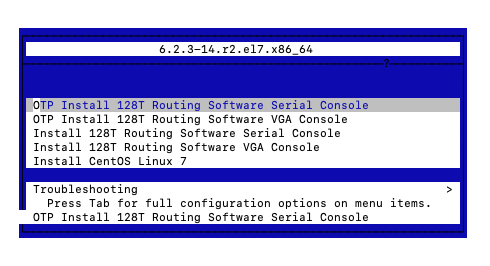
Selecting the wrong type of console may result in garbled characters being displayed. If allowed to continue it will result in an incorrect installation. If the wrong console is selected, reboot the target system and select the correct line for the target hardware.
For serial console issues please refer to Serial Console Troubleshooting.
- Press the TAB key to edit the configuration.
To enable FIPS Enforcement for SSR software version 6.2.5-5-sts, add the fips=1 kernel option to the kernel command line during system installation as shown in the steps below. This ensures that key generation is done with FIPS approved algorithms and continuous monitoring tests in place.
FIPS mode is required for Common Criteria compliance. Failure to configure FIPS mode, or the use of any other cryptographic engine nullifies compliance.
- Add
fips=1to the end of thevmlinuzparameters.
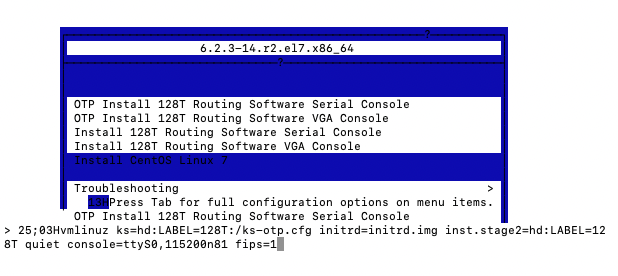
- Press Enter to start the install.
When you modify the GRUB kernel behavior by editing the GRUB menu at boot time, the changes do not persist over a system reboot. Default boot behavior is restored the next time you boot the system.
SSR Installation
This installation process is an automated workflow which does not require user interaction after selecting and initiating the OTP menu option. The system will power off after installation.
Enable Strict Host Key Checking
Enabling strict host-key-checking provides secure communication between the conductor and a router.
Similar to SSH, there are two host-key-checking options; yes which requires the host key to be provisioned manually, or accept-new which accepts the key on first connection.
There are two configuration parameters where host-key-checking can be set:
inter-router host-key-checkingcontrols host key verification between a router and the conductor. When set toyes, strict host key checking is enabled between the router and the conductor. However, the host keys must be manually provisioned on each router.
config authority router RTR_EAST_COMBO node combo-east-1 ssh-settings inter-router host-key-checking yes
config authority router RTR_EAST_COMBO node combo-east-2 ssh-settings inter-router host-key-checking yes
inter-node host-key-checkingcontrols host key verification between redundant HA nodes. When set toyes, strict host key checking is enabled between the router and the conductor between each node of an HA router. However, the host keys must be manually provisioned on each router.
config authority router RTR_EAST_COMBO node combo-east-1 ssh-settings inter-node host-key-checking yes
config authority router RTR_EAST_COMBO node combo-east-2 ssh-settings inter-node host-key-checking yes
To configure a new authorized key for ssh inter-node communication, use the create system connectivity authorized-keys command. This command adds an entry to the ssh authorized keys file.
Use the following show commands to display additional key information:
-
show system connectivity authorized-keysdisplays the authorized keys for ssh inter-node communication and tunneling. -
show system connectivity key-checking-modedisplays the key checking mode (Inter-Asset, Inter-Node, Inter-Router) across specified nodes.
To save the work of manually provisioning the host key on the router, set the accept-new parameter. This automatically loads the host key on first connection.
config authority router RTR_EAST_COMBO node combo-east-1 ssh-settings inter-router host-key-checking accept-new
Use the show system connectivity known-hosts to view the accepted host keys for the current node.
Manual Provisioning of the Conductor Key
If a router is configured for strict inter-router host-key-checking (set to yes), but does not have accept-new configured, it will be necessary to manually provision the conductor key prior to onboarding the router to the conductor. This will require the administrator to retrieve the host key of each node of the conductor and configure this in the router.
On the conductor, identify the key for each node using the command show system connectivity host-keys node all.
From the router PCLI, provision each conductor key using the following command:
create system connectivity known-hosts node <node> <conductor address> ssh-rsa <key> <comment>
<node>is the router node. The key should be added on each router node in an HA pair.<conductor address>is the conductor address. This should be added for each conductor address of an HA conductor pair.<key>is theKeyretrieved from the previous step.<comment>is an option that can be used to identify the key; for exampleConductor1.
The following example manually configures the key to the conductor node 192.168.1.13:
create system connectivity known-hosts router RTR_EAST_COMBO node combo-east-1 [192.168.1.13]:930 ssh-rsa <public key contents>
For additional information, see create system connectivity known-hosts.
Root Access
To permit root access to the SSR system, ensure that there is at least one user configured on each system with super user (sudo) privileges. Failure to do so may result in the loss of management connectivity to the router.
Logging in as root over SSH is not permitted.
Prerequisites for installation and upgrades now include configuring a super user in /etc/sudoers that is allowed to execute Linux shell commands as root (sudo privileges).
During an upgrade, if the existing version allows SSH Root login, it will be disabled. When a system is installed using the OTP ISO, a "t128" user is automatically configured with sudo privileges.
- Login using the admin credentials.
- Enter the Linux shell: Type
shellto suspend the CLI and enter the Linux shell. - Type
suand enter the default root password. - Use the following command to grant sudo privilege to the
adminuser account:/usr/sbin/visudo - Add an entry for admin as follows:
admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
- Save the file and exit from
visudo. - Type
exitto leave thesuprompt.
Change the Default Passwords
The following user accounts and passwords are created during the ISO installation process:
| Username | Password |
|---|---|
| root | 128tRoutes |
| t128 | 128tRoutes |
Change these passwords immediately. Use the passwd command from the Linux shell to individually set the password for each username.
[admin@localhost ~]$ sudo passwd t128
Changing password for user t128
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[admin@localhost ~]$ sudo passwd root
Changing password for user root.
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[admin@localhost ~]$
The root account will not be used for day-to-day access, but the root account password should be stored securely off-box so that it can be used for admin account recovery if required.
Software Compliance Validation
After installing the SSR Software, it is important to verify that the installation successfully completed and that the system is running in the FIPS enforcement mode required for Common Criteria compliance. After starting the SSR router or conductor, the login screen appears on the console. Alternatively you may ssh to the SSR management IP address using the admin account.
- Login using the admin credentials.
- Use
show system versionto verify the correct software release is running:
Last login: Thu Dec 14 13:28:36 UTC 2023 on pts/0
admin@conductor.conductor# show system version
Fri 2024-03-01 16:23:37 UTC
✔ Retrieving system version 1/1 targets complete...
=========== =========== ========= ======== ====================== =====================
Router Node Version Status Build Date Package
=========== =========== ========= ======== ====================== =====================
128t-east 128t-east 6.2.5 r2 2024-06-06T23:56:25Z 128T-6.2.5-5r2.el
7 (package based)
Completed in 0.05 seconds
admin@conductor.conductor#
It should report Version 6.2.5 and Status r2.
- Type
shellto suspend the CLI and enter the Linux shell. - Execute the command
sudo systemctl status 128Tand verify the service is listed asactive (running).
[root@conductor-test admin]# sudo systemctl status 128T -l
128T.service - 128T service
Loaded: loaded (usr/lib/systemd/system/128T.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2023-7-31 18:04:29 UTC; 50min ago
Main PID: 23317 (processManager)
- Perform the following steps to verify the software integrity and protect against future tampering:
- Execute the self-test scan
sudo systemctl start 128T-rpm-verify
The self-test scan is initiated and takes approximately two minutes to complete. Upon completion, run:
systemctl status 128T-rpm-verify
The scan validates all executable files on the system against the sha256 digest hash recorded in the signed RPMs from which they were installed. This ensures that no files have been replaced or tampered with.
- Run
systemctl status 128T-rpm-verifyto confirm that the service shows:
PASS: All RPM file digests verified
- If the result displays the following:
FAIL: RPM file digest mismatch detected
The failure must be resolved before continuing to ensure compliance. The full path to each file having a self-check digest mismatch is reported as part of the status output.
- After the self-test scan test has succeed, enable the automatic self-test by executing the
enablecommand in the linux shell:
sudo systemctl enable 128T-rpm-verify
The self-test is enabled on every subsequent reboot. If the self-test fails, the 128T service will not start.
-
Perform the following steps to verify that FIPS security enforcement mode is enabled in the OS:
openssl md5 /dev/nullExpected result:digital envelope routines … Disabled for fips -
Run the following command to verify that FIPS security enforcing mode is enabled in the kernel:
cat /proc/sys/crypto/fips_enabledExpected result:1 -
Type
exitto leave the Linux shell and return to the CLI. -
Type
quitto log out from CLI.
You have now completed security validation of the installation.
CLI Access Post Install
Use the following procedure to access the CLI at any time after installation.
- Open a terminal window and SSH to the SSR's IP address.
- Use your login credentials to log in to the SSR
-
If using an account other than admin, type
pclito start the SSR CLI. -
Type
shellto suspend the CLI and enter the Linux shell.
To terminate an active session:
-
Type
exitto return from the Linux shell to the CLI. -
Type
quitto log out from CLI. -
If using an account other than admin, type
exitto end the login session.
Common Criteria certification does not require any restrictions on executing commands. See the Configuration Command Reference Guide for command information and usage.