IPsec Client plugin
The 128T-ipsec-client plugin provides a way to send and encrypt traffic to IPsec endpoints through the SSR. It is possible to configure the plugin for each router to have multiple destination IPsec endpoints and thus the SSR will failover between them. This is accomplished by performing a Service Function Chain (SFC) with Libreswan, a third-party IPsec client. By enabling this plugin, you can provide IPsec tunnel connectivity to third party providers from your SSR.
The instructions for installing and managing the plugin can be found here.
Configuration
The IPsec plugin setup has the following key parts to the configuration.
ipsec-profiledescribing the mechanism with which to connect to the server.ipsec-clientrepresent the remote endpoints or server with which the ipsec client communicates.service-route's to route the traffic through the tunnels
Profiles
The router > ipsec-profile's are reusable IPsec settings that can be used across multiple nodes in a router and multiple IPsec endpoint remotes. The table below represents the most common configuration elements for a valid ipsec profile.
router
ipsec-profile zscaler
name zscaler
ike-encryption aes256
ike-digest sha2
ike-modp modp1024
authentication-protocol esp
phase2-encryption aes_gcm128
phase2-digest sha2
phase2-modp modp1024
ike-lifetime 1h
connection-lifetime 8h
perfect-forward-secrecy true
dpddelay 20
dpdtimeout 100
dpdaction restart
local-id [local-id@domain.com]
pre-shared-key (removed)
exit
exit
The above configuration example represents a typical profile used for a IPSec provider such as Zscaler. Please tune the settings to match the settings recommended by your provider.
| Config | Type | Recommended | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | - | The name of the profile |
| ike-encryption | enum | aes256 | Algorithm used for IKE encryption |
| ike-digest | enum | sha2 | Hash algorithm used for IKE encryption |
| ike-modp | enum | modp1024 | Modp group used for IKE encryption |
| authentication-protocol | enum | esp | The type of SA to be produced for authentication |
| phase2-encryption | enum | aes_gcm128 | Algorithm used for phase 2 encryption |
| phase2-digest | enum | sha2 | Hash algorithm used for phase 2 encryption |
| phase2-modp | enum | modp1024 | Modp group used for phase 2 encryption |
| ike-lifetime | time | 1h | Lifetime of the keying channel for a connection |
| connection-lifetime | time | 8h | Lifetime for the security association |
| perfect-forward-secrecy | bool | yes | Whether Perfect Forward Secrecy of keys is required on the connection |
| dpddelay | seconds | 20 | Delay between DPP keepalives on the connection |
| dpdtimeout | seconds | 100 | After the period has elapsed with no traffic including DPD traffic, the connection will be declared dead |
| dpdaction | enum | restart | Action taken once the enabled peer is detected as dead |
| local-id | string | user-defined | How to identify the router for authentication. Can be an IP address of FQDN. Must be preceded with an @ symbol to prevent resolution as shown in the example |
| pre-shared-key | string | user-defined | pre-shared key used for authentication |
This plugin can only connect to IPsec endpoints that support pre-shared key authentication.
Custom Options
Version History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.3.0 | profile > custom-option introduced |
The custom-option allows the user to configure additional obscure libreswan options that are not exposed via the profile and remote configuration.
config
authority
router myRouter
name myRouter
ipsec-profile myProfile
name myProfile
custom-option key
name key
value value
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
| Config | Description |
|---|---|
| name | The name of the libreswan option |
| value | The value of the option |
The custom-option is added to the libreswan config file; any invalid option could prevent the application from starting up.
Clients
Clients are a collection of remote endpoints which can be used for connection and failover purposes.
The main config properties of a remote endpoint are as follows.
| Config | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | string | The name of the remote client to be used for sending traffic to the tunnel. |
| host | ip-or-fqdn | The address or FQDN of the remote endpoint. |
| profile | reference | The name of the profile to be used for this remote endpoint. |
| remote-id | string | The optional remote identifier used during authentication. |
| subnet | ip-prefix | The remote subnet behind the tunnel. |
| tunnel-monitor | container | Properties for monitoring the phase-2 connection. See Tunnel Monitoring for more information. |
Example:
router myRouter
node
name myRouter
ipsec-client client1
name client1
enabled true
tenant ipsec
remote primary
name primary
host <primary-address>
profile myProfile
remote-id prisma@paloalto.com
subnet 0.0.0/0
tunnel-monitor
enabled true
destination 8.8.8.8
address 8.8.8.8
timeout 10
max-retries 3
interval 60
exit
exit
exit
remote secondary
name primary
host <primary-address>
profile myProfile
remote-id prisma@paloalto.com
subnet 0.0.0/0
tunnel-monitor
enabled true
destination 8.8.8.8
address 8.8.8.8
timeout 10
max-retries 3
interval 60
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
Only one ipsec-client can be configured per node, but two remotes can be configured per client.
The ipsec-client > name cannot start with ipsec or mast. See notes here.
Each remote represents a unique tunnel destination and can be used to route traffic in/out of the tunnels. Typically each node has two tunnels to act as primary and backup.
Tunnel Monitoring
Version History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.2.0 | remote > tunnel-monitor introduced |
| 3.6.0 | remote > tunnel-monitor > source introduced |
Tunnel monitoring is a way to monitor the health of individual tunnels and have them automatically restart if they become unhealthy. An ICMP ping is used for the traffic. For each remote, you can specify a destination, interval, timeout, and the number of max retries for each interval.
node
ipsec-client client1
remote c1gateway1
tunnel-monitor
enabled true
destination 8.8.8.8
address 8.8.8.8
timeout 10
max-retries 3
interval 120
exit
exit
exit
tunnel-monitor-nat-network 10.128.128.0/28
exit
exit
| Config | Description |
|---|---|
enabled | Allows you to switch tunnel monitoring on and off for a remote. |
source | Optional source-ip to be used for originating the tunnel monitoring pings. |
address | The IP or hostname where traffic is sent. This address must be reachable after traversing the tunnel. |
timeout | Duration (in seconds) within which to reach the destination. Each attempt will be made in this duration / max-retries interval. |
max-retries | Number of consecutive missed ICMP ping responses from the destination within the interval before deciding that the tunnel is unhealthy. |
interval | Duration (in seconds) of how often to perform an ICMP probe test to the probe-address. |
tunnel-monitor-nat-network | The subnet where traffic originates. The corresponding ingress KNI's fourth octet is used. By default, the subnet 10.128.128.0/28 is used. |
Configuring services for tunnel traffic
The user can define up to four ipsec-client > remote endpoints per node. In addition, the user must also define the necessary service and service-routes to route the tunnel traffic over the desired WAN interface.
The following example shows a configuration for capturing the egress tunnel traffic and allows the ipsec tenant as defined in router > ipsec-client > tenant config above.
config
authority
service ipsec-tunnel
name ipsec-tunnel
scope private
address <remote-address-1>
address <remote-address-2>
transport udp
protocol udp
port-range 4500
start-port 4500
exit
port-range 500
start-port 500
exit
exit
access-policy ipsec
source ipsec
exit
exit
exit
exit
The <remote-address-1> and <remote-address-2> represent the node > ipsec-client > remote > host address. The ipsec tenant is allowed as per the tenant defined under ipsec-client > tenant. The user can split the tunnels into separate services per the routing requirements.
Session Record
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.6.0 | Support for leveraging session-record was introduced |
Various features introduced as part of the 3.6.0 version require the user to enable session records on the egress tunnel services such as ipsec-tunnel shown above. The following sample config shows the recommend profile that can be configured and associated with the egress tunnel service.
config
authority
session-record-profile ipsec-profile
name ipsec-profile
include-start-record true
include-modify-record true
exit
service ipsec-tunnel
name ipsec-tunnel
session-record
profile ipsec-profile
exit
exit
exit
exit
Once enabled, the records will allow the IPsec controller to perform additional functions such as detecting and remediating stuck egress tunnel sessions and reporting the name of the WAN interface being used for the tunnel.
Directing traffic through the tunnel
The user can leverage standard SSR service and service-route to direct intended traffic over the ipsec tunnel. In the example below, all guest internet traffic is sent over the ipsec tunnel for break and inspect. This can be accomplished as follows:
config
authority
router myRouter
name myRouter
service-route guest-internet-rte-primary
name guest-internet-rte-primary
service-name guest-internet
next-hop combo-east-1 primary
node-name combo-east-1
interface primary
exit
exit
service-route guest-internet-rte-secondary
name guest-internet-rte-secondary
service-name guest-internet
next-hop combo-east-1 secondary
node-name combo-east-1
interface secondary
exit
exit
exit
tenant guest
name guest
exit
service guest-internet
name guest-internet
description "guest-internet access"
scope private
address 0.0.0.0/0
access-policy guest
source guest
exit
exit
exit
exit
The service-route > next-hop > interface must point to the corresponding ipsec-client > remote > name-intf to route the traffic through the tunnel. All available SSR routing techniques including using vectors, service-policy, etc., can be leveraged to define how the untrusted traffic is sent over the tunnels, and how to route the traffic. The SSR routes the packets through the appropriate IPSec tunnels and manages the failover as per the policy. On the return path, the encrypted traffic is processed, decrypted, and send back to the client that originated the session.
Redundancy
By default both nodes of an HA pair will create and maintain the tunnels configured for them.
Version History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.5.0 | Introduced Active-Standby |
Active-Standby
This mode of operation can be configured on a per router basis under router > ipsec.
| Config | Description |
|---|---|
redundancy-enabled | Turns on the active-standby mode of operation. The default is false. |
redundancy-interval | How often to check for a failover when in active-standby mode (in seconds). The default is 1 second. |
Thirdparty Software & Licenses
Version History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.5.0 | libreswan-3.28-1 |
| 1.0.0 | libreswan-3.23-5 |
- Libreswan v3.28-1.el7_5 (GNU GPLv2)
Troubleshooting
Data Model
If the data model doesn’t appear in the PCLI or GUI, make sure that you have restarted the SSR service.
Logging
The /var/log/128technology/persistentDataManager.log file at trace level will hold whether the configuration generation was run as well as output and return code.
The /var/log/128technology/automatedProvisioner.log file at trace level will hold whether the pillar generation was run as well as output and return code.
Configuration and pillar generation logs can be found on the conductor under /var/log/128technology/plugins/ipsec-client-config-generation.log and /var/log/128technology/plugins/ipsec-client-pillar-generation.log respectively.
Salt
Salt status can be found on the conductor by utilizing the PCLI’s show assets and show assets <asset-id> commands.
PCLI Enhancements
Version History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.5.0 | Enhanced output |
To check the status of the IPsec tunnels for a given ingress KNI, extra IPsec tunnel related output will be found in the show device-interface command as well as the show plugin state command.
Example output for a healthy tunnel:
admin@combo-west.RTR_WEST_COMBO# show device-interface name rem2
Tue 2020-06-30 16:44:39 UTC
=========================================================
combo-west:rem2
=========================================================
Type: host
Forwarding: true
Mode: host
MAC Address: 22:ee:4e:b6:37:a8
Admin Status: up
Operational Status: up
Redundancy Status: non-redundant
Speed: 1000
Duplex: full
in-octets: 9992
in-unicast-pkts: 161
in-errors: 0
out-octets: 6986
out-unicast-pkts: 161
out-errors: 11
IPSec:
rem2:
Tunnel Status:Up
Tunnel Details:
Name: ipsec-client-tunnel-secondary-rem2
Remote Host:172.16.5.4
Remote id:172.16.5.4
SA Details:
Add time:2023-03-14 18:05:03
In bytes:0
Out bytes:0
Ingress Bytes:3846598
Ingress Packets:85732
Egress Bytes:5344740
Egress Packets:85857
IKE Version:2
IKE Algorithm Elected:AES_CBC_128-HMAC_SHA1-MODP1024
ESP Algorithm Elected:NULL_000-HMAC_MD5_96
SA Count: 1
Up Since: 2023-03-10 04:04:08.768292
Completed in 0.12 seconds
Example output for a tunnel that is down:
========================================
combo-west:rem1
========================================
Type: host
Forwarding: true
Mode: host
MAC Address: 76:78:79:fc:eb:69
Admin Status: up
Operational Status: down
Redundancy Status: non-redundant
Speed: 0
Duplex: unknown
in-octets: 1962932
in-unicast-pkts: 32710
in-errors: 0
out-octets: 1373442
out-unicast-pkts: 32701
out-errors: 6
IPSec:
rem1:
Tunnel Status:Down
Tunnel Details:
Name: ipsec-client-tunnel-primary-rem1
Remote Host:172.16.4.3
Down Reason: No response from Remote Host
Tunnel Monitor State
If tunnel monitoring is enabled for a remote, corresponding tunnel monitoring state is included in the pcli commands.
IPSec:
rem2:
Tunnel Status:Up
Tunnel Details:
Name: ipsec-client-tunnel-secondary-rem2
Remote Host:172.16.5.4
Remote id:172.16.5.4
SA Details:
Add time:2023-03-14 18:05:03
In bytes:0
Out bytes:0
Ingress Bytes:3846598
Ingress Packets:85732
Egress Bytes:5344740
Egress Packets:85857
IKE Version:2
IKE Algorithm Elected:AES_CBC_128-HMAC_SHA1-MODP1024
ESP Algorithm Elected:NULL_000-HMAC_MD5_96
SA Count: 1
Up Since: 2023-03-10 04:04:08.768292
Tunnel Monitoring:
Destination:8.8.8.8
Status: up
Last Attempt:2022-02-14 15:42:34
Last Restart:2022-02-14 15:41:15
Metrics
Non-persistent metrics were added for the ingress/egress packets/bytes of the tunnels.
# show stats ipsec-client
Tue 2023-03-14 18:50:47 UTC
✔ Retrieving statistics...
IPSec Client Metrics
--------------------
================== ============ ======== =========
Metric Node Remote Value
================== ============ ======== =========
received bytes combo-west rem1 0
combo-west rem2 3854998
received packets combo-west rem1 0
combo-west rem2 85932
sent bytes combo-west rem1 9662
combo-west rem2 5356740
sent packets combo-west rem1 136
combo-west rem2 86057
Completed in 0.12 seconds
Commands
Version History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.3.0 | restart ipsec remote command was introduced |
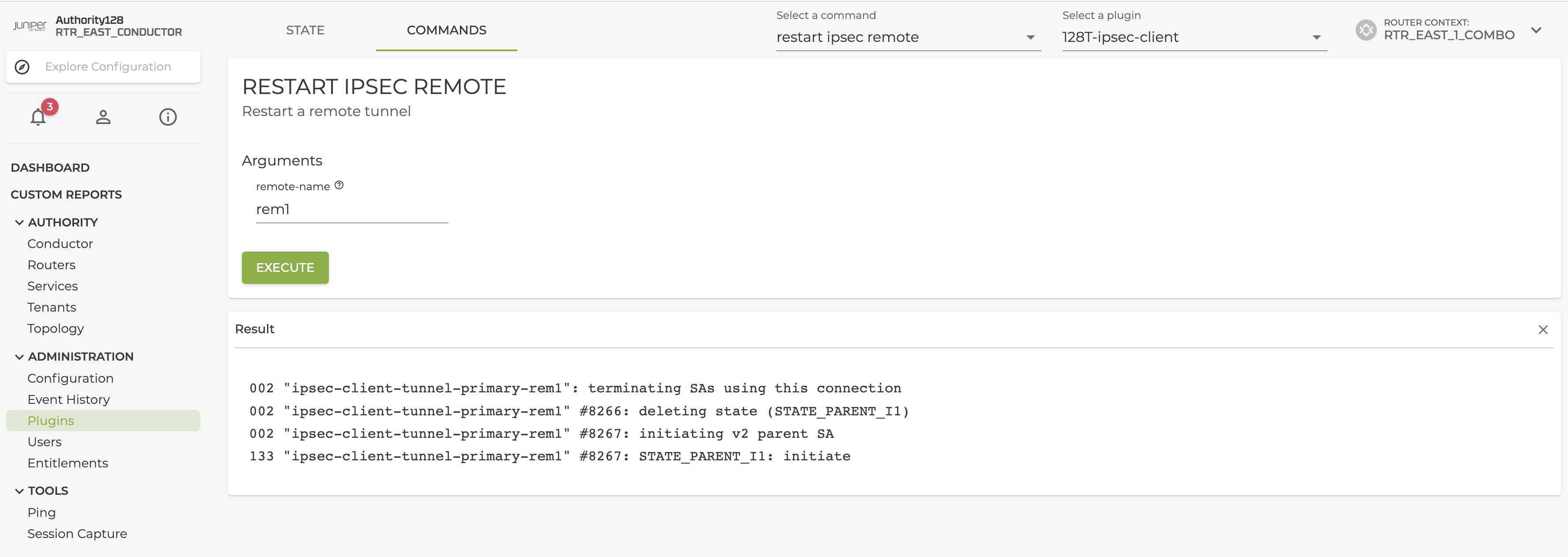
The restart ipsec remote command can be used to restart an individual IPSec tunnel via the conductor PCLI and UI.
admin@node1.conductor# restart ipsec remote router router-1 node node-1 remote-1
✔ Retrieving 0/1 targets complete....
Target: node1.conductor
002 "ipsec-client-tunnel-primary-remote-1": terminating SAs using this connection
002 "ipsec-client-tunnel-primary-remote-1" #8261: deleting state (STATE_PARENT_I1)
002 "ipsec-client-tunnel-primary-remote-1" #8262: initiating v2 parent SA
133 "ipsec-client-tunnel-primary-remote-1" #8262: STATE_PARENT_I1: initiate
Successfully retrieved info.
admin@node1.conductor#
From the conductor UI, the command can be accessed as shown in the screenshot below.
Systemd Services
To check the status of the IPsec client service on the router, you can run show system services which will show all SSR related services running on the specified node. The one for this plugin is named 128t-ipsec.
To verify that the services are running properly on the SSR:
systemctl status 128t-ipsec@<client>.service
Failover Alarms
If a tunnel goes down, we set the corresponding ingress KNI to be operationally down. An alarm will be created when this happens.
Example output when the tunnel for rem1 goes down:
admin@combo-west.RTR_WEST_COMBO# show alarms
Tue 2020-06-30 16:42:50 UTC
============== ===================== ========== ============= =========== ==================================
ID Time Severity Source Category Message
============== ===================== ========== ============= =========== ==================================
combo-west:8 2020-06-30 16:32:42 critical unavailable interface Intf rem1 (4) operationally down
There are 0 shelved alarms
Completed in 0.10 seconds
Appendix
Generated SSR Configuration
A KNI per remote is created with the name of the remote and a single egress KNI is created with the name of the ipsec-client.
User-Specific SSR Configuration
To allow the maximum flexibility on getting the traffic into the plugin's network namespace and getting the traffic out, we rely on the user to configure those means (usually through services and service routes).
You will need to have the IPsec endpoint bound traffic sent into the KNIs with the names of the remotes. You can use builtin SSR failover techniques due to the KNIs being reported operationally down when the corresponding tunnel is down. You will also need to configure a way for the traffic to be routed towards the IPsec endpoint after being encrypted. All of this encrypted traffic will be assigned to the tenant configured under ipsec-client.
Complete Example Configuration
Below is an example of a complete, but minimal configuration entered by the user.
This example configuration is good to understand all of the concepts but should not be used on a system as is.
config
authority
tenant ipsec
exit
tenant lan
exit
service cleartext
name cleartext
address 1.1.1.0/24
access-policy lan
source lan
permission allow
exit
exit
service ipsec
name ipsec
address 172.16.4.3
access-policy ipsec
source ipsec
permission allow
exit
exit
router router1
ipsec-profile primary
name primary
pre-shared-key somekey1
exit
ipsec-profile secondary
name secondary
pre-shared-key somekey2
exit
node node1
device-interface lan
name lan
network-interface lanintf
name lanintf
tenant lan
address 172.16.1.2
ip-address 172.16.1.2
prefix-length 24
gateway 2.2.2.1
exit
exit
exit
device-interface wan
name wan
network-interface wanintf
name wanintf
address 172.16.3.2
ip-address 172.16.3.2
prefix-length 24
gateway 172.16.3.5
exit
exit
exit
ipsec-client client1
name client1
enabled true
tenant ipsec
remote rem1
name rem1
host 172.16.4.3
profile primary
exit
remote rem2
name rem2
host 172.16.5.4
profile secondary
exit
exit
exit
service-route rem1
name rem1
service-name cleartext
next-hop router1 rem1-intf
node-name router1
interface rem1-intf
gateway-ip 169.254.129.6
exit
exit
service-route rem2
name rem2
service-name cleartext
next-hop router1 rem2-intf
node-name router1
interface rem2-intf
gateway-ip 169.254.129.10
exit
exit
service-route ipsec
name ipsec
service-name ipsec
next-hop router1 wanintf
node-name router1
interface wanintf
gateway-ip 172.16.3.5
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
Upon commit, the plugin will generate other configuration as shown below:
config
authority
router router1
node node1
device-interface client1
name client1
description "Auto-generated host interface for use with ipsec-client"
type host
network-namespace client1
network-interface client1-intf
name client1-intf
type external
tenant ipsec
address 169.254.129.1
ip-address 169.254.129.1
prefix-length 30
gateway 169.254.129.2
exit
exit
exit
device-interface rem1
name rem1
description "Auto-generated host interface for use with ipsec-client"
type host
network-namespace client1
network-interface rem1-intf
name rem1-intf
type external
tenant _internal_
address 169.254.129.5
ip-address 169.254.129.5
prefix-length 30
gateway 169.254.129.6
exit
exit
exit
device-interface rem2
name rem2
description "Auto-generated host interface for use with ipsec-client"
type host
network-namespace client1
network-interface rem2-intf
name rem2-intf
type external
tenant _internal_
address 169.254.129.9
ip-address 169.254.129.9
prefix-length 30
gateway 169.254.129.10
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
Release Notes
Release 5.0.0
New Features and Improvements
Support for install and upgrade of a customized upstream Linux-based SSR OS distribution for 7.0 and above.
On conductor, the plugin will auto upgrade to this version when upgrading from 6.x to 7.x version of SSR software. In addition, all routers will also be auto upgraded to their respective Oracle Linux 7 or Oracle Linux 9 plugin version depending on the SSR version running on the device.
Release Date: Oct 13, 2025
Release 4.2.0
Release Date: Sept 15, 2025
New Features and Improvements
- PLUGIN-3014 Add debug log-level in configuration per router for simplified troubleshooting
- PLUGIN-3016 Improve tunnel status monitoring and reporting of issues through existing state commands
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-3059 Resolve ping-monitor restart issue after upgrade
Release 4.1.1
Release Date: Apr 30, 2025
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-2959 Resolve copying unncessary files on image-based upgrade
Release 4.1.0
Release Date: Feb 27, 2025
New Features and Improvements
- PLUGIN-2780 Support multiple algorithms per tunnel for IKE and Phase2 settings.
- PLUGIN-2782 Deprecate modp1024 algorithm that is less secure. Starting in IPSec 5.0; modp1024 algorithms will be removed completely.
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-2721 Resolve configuration removal after plugin downgrade
Resolution: Increase plugin-support-files minimum dependency.
-
WAN-2528 Improve tunnel startup
Resolution: IPSec Controller handles restarts/upgrades/errors more gracefully.
-
MIST-136625 Memory Increasing for IPSec Plugin
Resolution: Properly cleanup journal command processes when they are no longer valid.
-
PLUGIN-2891 Received 500 for tunnel status command
Resolution: Handle missing state data for tunnels due to "down" state and return valid data.
Release 4.0.1
Release Date: Oct 31, 2024
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-2721 Resolve on plugin downgrade config removal
Release 4.0.0
Image based install and upgrade (IBU) support for SSR 6.3.0.
Release Date: Sep 30, 2024
Release 3.6.2
Release Date: Aug 7th, 2024
Router Version 128T-ipsec-2.4.4-2
Issues Fixed
-
WAN-3229 IPSec tunnels can restart due to unrelated config changes.
Resolution: IPSec config handler manages the config changes more gracefully to avoid spurious restarts.
-
WAN-3334 IPSec tunnels can sometimes fail to start on boot.
Resolution: The pluto runtime directories are created dynamically to avoid certain types of startup failures.
-
PLUGIN-2490 IPSec plugin validation shows incorrect warning about empty local-id
Resolution: The validation logic was made more robust to better handle cases for empty and existing configuration.
-
PLUGIN-2550 IPSec plugin causing monitoring script to get stuck forever
Resolution: The DNS resolution from IPSec namespace enforces better controls and limits to avoid a startup race condition due to which the monitoring script was getting stuck forever. The graceful handling would prevent other scripts from getting stuck indefinetly.
Release 3.6.1
Release Date: May 29, 2024
Router Version 128T-ipsec-2.4.3-2
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-2232 Configured and enabled tunnels remain down.
Resolution: File corruption is now handled more gracefully, preventing IPSEC tunnels from going down.
-
PLUGIN-2197 DNS resolution failure causes plugin to become stuck.
Resolution: When FQDNs are defined in the
ipsec-client>remote>hostfields, the plugin will not start the tunnels if the FQDNs of the tunnels are unresolvable. -
WAN-1848 Tunnel monitoring failures did not cause traffic failover to other tunnels.
Resolution: If tunnel monitoring is configured, the tunnel monitoring status will be tied into the ingress KNI's operational status which will cause traffic to failover.
-
WAN-2648 Excessive logging in
ipsec-controllerjournal.Resolution: Reduced logging to provide a simplified journal.
-
WAN-2994 Port 500 sessions were stuck even with session deletion feature.
Resolution: Delete the port 500 and 4500 sessions whenever the tunnel does not come up.
Release 3.6.0
Release Date: Oct 13, 2023
Router Version 128T-ipsec-2.4.0-4
New Features and Improvements
- WAN-2815 Improve the memory and cpu consumption of the IPsec plugin on the router
For the IPsec plugin, several individual processes were consolidated into a single controller process providing an overall reduction in CPU and memory when the plugin is enabled on an SSR.
- I95-50410 SSR VPN to Azure interface not working due to a stuck session
The new version adds support for automatically detecting egress tunnel sessions that are not able to communicate with the IPsec remote server anymore. The recovery happens in the form of automatically deleting those sessions allowing new egress tunnel sessions to be formed. Please refer to the session-record section on how to enable this new feature.
- WAN-2361 Include the egress wan interface being used for ipsec tunnel for better tunnel insights
Please refer to the session-record section on how to enable this new feature.
- WAN-1847 Support for custom source-ip for tunnel-monitoring
The new version simplifies the configuration for specifying a source ip to be used for the tunnel-monitoring feature.
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-1999 MTU and auto-mss adjustment not working for IPsec tunnel KNIs.
Resolution: The
mtuconfiguration is not correctly reflected on the tunnel KNIs as well as the underlying libreswan config. -
I95-49643 Tunnel has been flapping constantly and dropping traffic.
Resolution: When dead-peer detection triggers on an IPsec connection using multiple left and/or right subnets the tunnels will be automatically restarted to avoid an issue encountered with the third-party code.
Release 3.5.0
Release Date: Mar 17, 2023
Router Version 128T-ipsec-2.3.0-4
New Features and Improvements
- WAN-1298 Upgrade libreswan version
Upgraded from 3.23-5 to 3.28-1.
- PLUGIN-1981 Enhance the plugin state output for better insights into the tunnels
The plugin now supports more helpful plugin state output such as:
- Down reason
- Chosen ike proposal
- Chosen ipsec proposal
- More accurate uptime
- More accurate ingress/egress bytes/packets
- Ike version
Example output can be found in the PCLI Enhancements section.
- PLUGIN-1911 Support an active-standby HA mode
The plugin now supports the redundancy-enabled configuration option. This ensures that tunnels are being created by only one node at a time. The default behavior remains active-active.
- PLUGIN-1913 Add metrics for tunnel statistics
The plugin now supports non-persisted metrics for tunnels. More details and examples can be found in the Metrics section.
- PLUGIN-1996 WAN Assurance 1.0 will display conductor managed ipsec tunnels
When using the 128T-ipsec-client and 128T-mist-wan-assurance plugins together, ipsec tunnel details will show up in the Mist UI.
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-1999 Tunnels failed to come up because of unresolvable DNS during startup
Resolution: The salt application no longer requires DNS to generate libreswan configuration.
-
PLUGIN-1906 DNS Proxy services were not being used for ipsec hostname resolution
Resolution The plugin now automatically adds the configured ipsec tenant to dns-proxy services.
-
PLUGIN-1782 Removing destinations from tunnel monitoring config causes invalid configuration
Resolution The configuration validation now accepts this configuration flow
Release 3.4.1
A bug fix release that is only compatible with SSR < 6.3.
Release Date: Dec 11, 2024
Router Version 128T-ipsec-2.2.5-2
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-2833 Tunnels can flap due to rekey when connecting to some servers.
Resolution: Release ipsec client with libreswan-3.23 compatability that is known to not have rekeying issues with some servers.
-
WAN-3229 IPSec tunnels can restart due to unrelated config changes.
Resolution: IPSec config handler manages the config changes more gracefully to avoid spurious restarts.
Release 3.4.0
Release Date: Jul 13, 2022
Router Version 128T-ipsec-2.2.4-2
New Features and Improvements
- PLUGIN-1720 Added support for new ciphers for Phase-1 and Phase-2 security
The plugin now support aes-256-gcm, dh-20, sha512 and no-auth encryption schemes.
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-880 IPSec client connection is not initiated for certain config combinations
Resolution: The ipsec client names beginning with ipsec and mast are not supported by libreswan. As part of the fix, a new config rule was added to enforce this requirement.
-
PLUGIN-1807 IPSec health monitoring configuration does not report correct status
Resolution: The monitoring scripts were writing data to a non-persistent path resulting in the failure across reboots. The state directory will not be automatically re-generated on system reboots.
-
PLUGIN-1810 Trace logging in configuration results in IPSec failures
Resolution: Trace level logging is now converted appropriately for IPSec configuration to prevent underlying failures.
Release 3.3.1
Release Date: May 25, 2022
Router Version 128T-ipsec-2.2.2-1
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-1730 Invalid libreswan configuration was being generated when multiple local or remote subnets were configured.
Resolution The issue with the libreswan configuration generation has been resolved.
Release 3.3.0
Release Date: Apr 27, 2022
New Features and Improvements
- PLUGIN-630 Raise the number of supported IPSec client tunnels from 2 to 4
The plugin now supports up to 4 IPSec tunnels per node.
- PLUGIN-1641 Optimize the initial IPSec environment setup
The majority of the IPSec config and environment management is performed locally on the router thereby minimizing the interaction with salt states.
- PLUGIN-1533 Create a command to restart an individual tunnel
A new command was added to allow the user to restart an individual tunnel. More details can be found in the commands section
- PLUGIN-1532 Enable additional configuration options for IPSec tunnels.
The encapsulation and remote-peer-type options are now available for configuration.
- PLUGIN-1554 Collect ipsec-client plugin data as part of tech support info
The detailed tech support info bundle will now include the necessary logs and data for troubleshooting ipsec-client plugin related problems.
- PLUGIN-1598 - Support custom options for obscure libreswan config fields
A new config option has been added to enable libreswan features that are not made available as first class configuration.
- PLUGIN-1591 Add cpu, memory, and status tracking for ipsec services.
The system will now track the cpu, memory and usage information for various IPSec client related processes.
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-1628 Incorrect network-script path was being used in the auto generated device-interface configuration
Resolution The auto configuration was updated to use the correct script path.
-
PLUGIN-1610 The IPSec environment setup can fail on first time plugin install
Resolution The salt states were improved to have better interdependencies to avoid the first time boot failure.
Release 3.2.0
New Features and Improvements
- PLUGIN-1509 Ability to configure tunnel monitors
The feature adds support for configuring tunnel monitors using ping. See the tunnel monitoring section for more details.
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-1389 Corrupt encryption database caused tunnels to not come up.
Resolution The service on the router will clean up these database files on startup.
-
PLUGIN-1467 Configuring
aes_gcm256forphase2-encryptionresulted in invalid libreswan configuration.Resolution The libreswan config generation will generate valid configuration for
aes_gcm256.
Release 3.1.3
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-1480 IPSec tunnels were removed from all previously configured routers after config commit
Resolution: The config generation logic for the plugin will handle config with long lines correctly
Release 2.2.0, 3.1.0
New Features and Improvements
- PLUGIN-1289 Ability to provision custom MSS on the remote tunnel interfaces
The feature adds support for configuring a custom MSS value on the remote IPSec tunnel interface. The new configuration can be found under router > node > ipsec-client > remote > enforced-mss. The configuration follows the same format as the network-interface > enforced-mss.
Release 1.0.7, 2.0.7, 2.1.0, 3.0.2
Issues Fixed
-
PLUGIN-1092 IPSec left and right subnet configuration does not always work correctly
Resolution: The non-default left and right subnet configuration is correctly translated to corresponding libreswan configuration.
-
PLUGIN-1103 IPSec remote host does not appear as link on the GUI
Resolution: The GUI presentation model was updated to include the missing key field.
Release 3.0.1
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-1092 Added fix for local and remote subnet configuration option to allow a single value or a list of values.
Release 3.0.0
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-768 Support the IPSec client plugin in SSR versions
5.1.0and greater. - PLUGIN-611 Added support for plugin state. Plugin state information can be accessed on the PCLI using
show plugins state [router <router>] [node <node>] [{detail | summmary}] 128T-ipsec-client
Release 1.0.6, 2.0.6
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-1057 Ensure all critical IPsec client directories are created during installation of the plugin.
- PLUGIN-1053 Added an inactive IPsec client plugin state to allow seamless migration from zscaler. The inactive state is achieved by excluding
ipsec-clientfrom the configuration. - PLUGIN-1046 Provide IPsec client auto-upgrade capability while crossing the SSR version
4.3.0boundary.
Release 1.0.5, 2.0.5
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-994 The
ipsec-client > remote-idconfiguration is not being used correctly when generating the libreswan config.
Release 1.0.4, 2.0.4
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-384 Added an MTU configuration option to the ipsec profile.
- PLUGIN-333 The
plugin-networkip prefix setting in the configuration was ignored and would instead use the default ip prefix setting. - PLUGIN-336 Using the
vector-nameconfiguration option would generate invalid configuration. - PLUGIN-400 Added a local subnet configuration option and enhanced the remote subnet configuration option to allow a list of values.
Release 1.0.1, 2.0.1
Issues Fixed
- PLUGIN-47 Created generic IPsec client plugin to provide connectivity to remote ipsec endpoints. This version supports a single client with up to two remote endpoints.