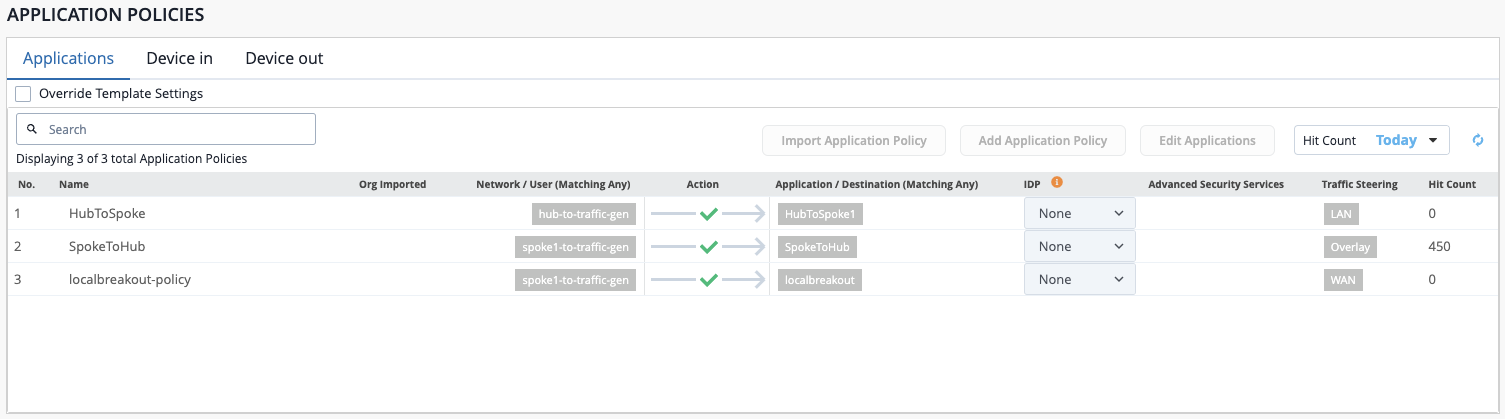
Application Policy Hit Count
Application Policy Hit Count (APHC) provides insight into the routing policies being used to direct traffic in your network operations; it reports which policies are seeing active traffic ("hit") and how. These values are presented as metrics tracked per service, per tenant; where each tenant service combination could be "hit" in one of the following ways.
| Count | Description |
|---|---|
| Allowed | The session was allowed and created successfully. |
| Failed | The session could not be created. |
| Denied due to Access Policy | The packet was denied because an access policy explicitly disallows access. |
| Denied due to URL Filtering | The session was created but was blocked once app classification was completed. |
| Denied due to Local Service Definition | The session was allowed on another ingress router, but is denied here based on the policy on this router (commonly related to hierarchical services). |
How Does It Work?
Application Policy Hit Count is enabled by default, tracking counts for all observed service and tenant combinations, including the access policy denied counters.
The system maintains the current value in memory and will not provide a historical time series of the data unless configured to do so. To prevent excessive consumption of memory resources, the device periodically removes combinations that are no longer being observed. Inactive tenant service combinations remain in the system for 30 to 60 minutes before being removed.
Configuration
Counter configuration is flexible and can be enabled or disabled on individual routers, or across the whole authority. Counters can be configured to persist the policy hit count metrics, allowing them to be viewed as a time-series graph. The following configuration snippets show how each configure each option.
Disable APHC for the Authority
configure
authority
metrics
application-policy-hit-count-tracking
enabled false
exit
exit
exit
exit
Disable APHC for the Router
configure
authority
router <router>
system
metrics
application-policy-hit-count-tracking disabled
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
Disable APHC for the Authority but Enable for a Specific Router
configure
authority
metrics
application-policy-hit-count-tracking
enabled false
exit
exit
router <router>
system
metrics
application-policy-hit-count-tracking enabled
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
Clear Expiring Counts
The cleanup of expired counters runs automatically every 30 minutes. However, in some situations it may be necessary to manually clear hit count entries. In this situation the following command is available:.
clear application-policy-hit-counts [force] [node <node>] {router <router> | resource-group <resource-group>}
This command manually triggers the cleanup process. The execution does not change or prevent the scheduled cleanup run. However, executing the command twice will move cleanup forward by an hour and fully clear the policy hit count metrics.
Persist APHC Metrics
Persistence can be configured using a metrics profile as described in the SSR Documentation. The example below show how to persist all hit count types for a specific service and tenant combination, using the short retention policy. It is a best practice to always use the shortest retention policy that satisfies your requirements.
There are typically a significant number of APHC metrics active on a system. If persistence is necessary, select a small number of service tenant combinations to be persisted. Careless selection may overwhelm the stats infrastructure resulting in resource shortages.
The following configurations are examples only; they should not be directly copied into another environment. Service, tenant, and router names must be replaced.
Authority Configuration
configure
authority
metrics-profile internet-policy-hit-counts
name internet-policy-hit-counts
metric /stats/application-policy-hit-count/allowed
id /stats/application-policy-hit-count/allowed
description "Allowed Hit Count"
exit
metric /stats/application-policy-hit-count/failed
id /stats/application-policy-hit-count/failed
description "Failed Hit Count"
exit
metric /stats/application-policy-hit-count/deny/policy-table
id /stats/application-policy-hit-count/deny/policy-table
description "Denied for Explicit Access Policy Hit Count"
exit
metric /stats/application-policy-hit-count/deny/local-service
id /stats/application-policy-hit-count/deny/local-service
description "Denied After Ingress Router Allowed Hit Count"
exit
metric /stats/application-policy-hit-count/deny/url-filtering
id /stats/application-policy-hit-count/deny/url-filtering
description "Denied For URL Filtering Hit count"
exit
filter service
parameter service
value internet
exit
filter tenant
parameter tenant
value engineering
exit
exit
exit
exit
Router Configuration
configure
authority
router <router>
name <router>
system
metrics
profile internet-policy-hit-counts
name internet-policy-hit-counts
retention short
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
exit
Stats Output
The hit count metrics can be accessed via the PCLI as shown. They provide a combination of services and tenants and show how traffic is allowed or blocked. In the example shown, we also see failures due to improperly configured services.
admin@westB.T207_West# show stats application-policy-hit-count node westA
Wed 2025-01-08 18:59:28 UTC
✔ Retrieving statistics...
Highway Manager application policy hit count Stats
--------------------------------------------------
========= ======= ================= ================== =======
Metric Node Tenant Service Value
========= ======= ================= ================== =======
allowed westA <global> lan2-service 1
westA red lan2-service 1
westA red lan2-service 326
deleted westA <global> lan2-service 1
failed westA <invalidTenant> <UnknownService> 11
westA red <UnknownService> 5841
Completed in 0.06 seconds
Application Policy Hit Count - Mist Output