Customizable Firewall Rules and Filters
As part of the security hardening and certification process, the SSR has implemented the following firewall features to provide a more secure platform for network traffic. Steps for configuration from both the GUI and the PCLI are provided.
Revision History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 6.2.3-R2 | Features and settings described here introduced |
Packet Filtering
The SSR uses Berkeley Packet Filters (BPF) to create customizable firewall filters. This filtering solution can be a key tool to prevent packet level attacks and aid with intrusion detection and prevention. Using BPF, packets on the SSR can be filtered by any known packet field, and the order in which filters are applied can be set by the user. Filters are configured and applied on the receiving network-interface.
Configure using the GUI:
- At the Authority level, select the router, then the node, the device interface, and the network interface where the filters will be configured.
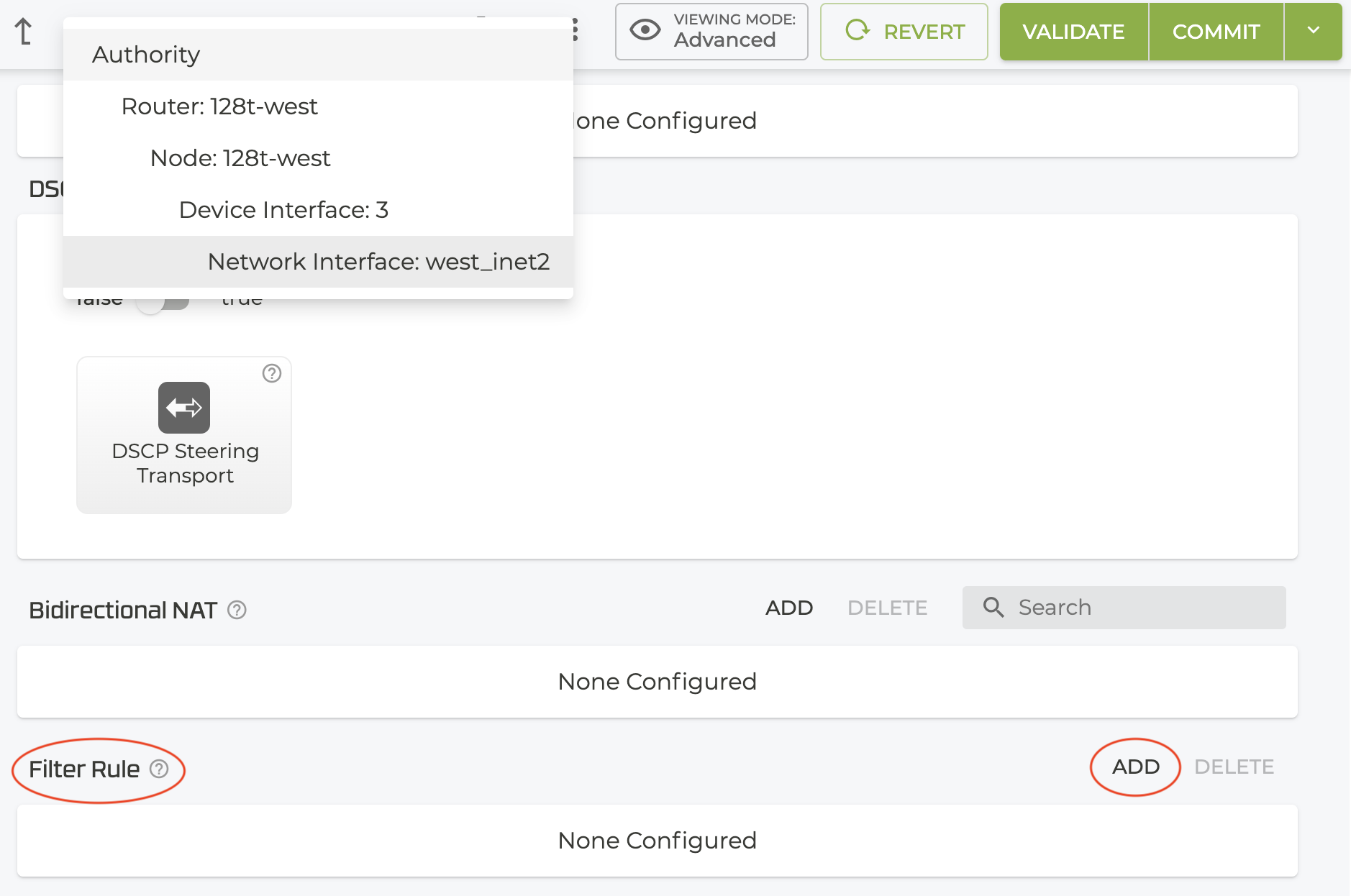
-
Scroll down to the Filter Rule panel.
-
Click Add.
-
In the New Item window, name the rule and click SAVE.

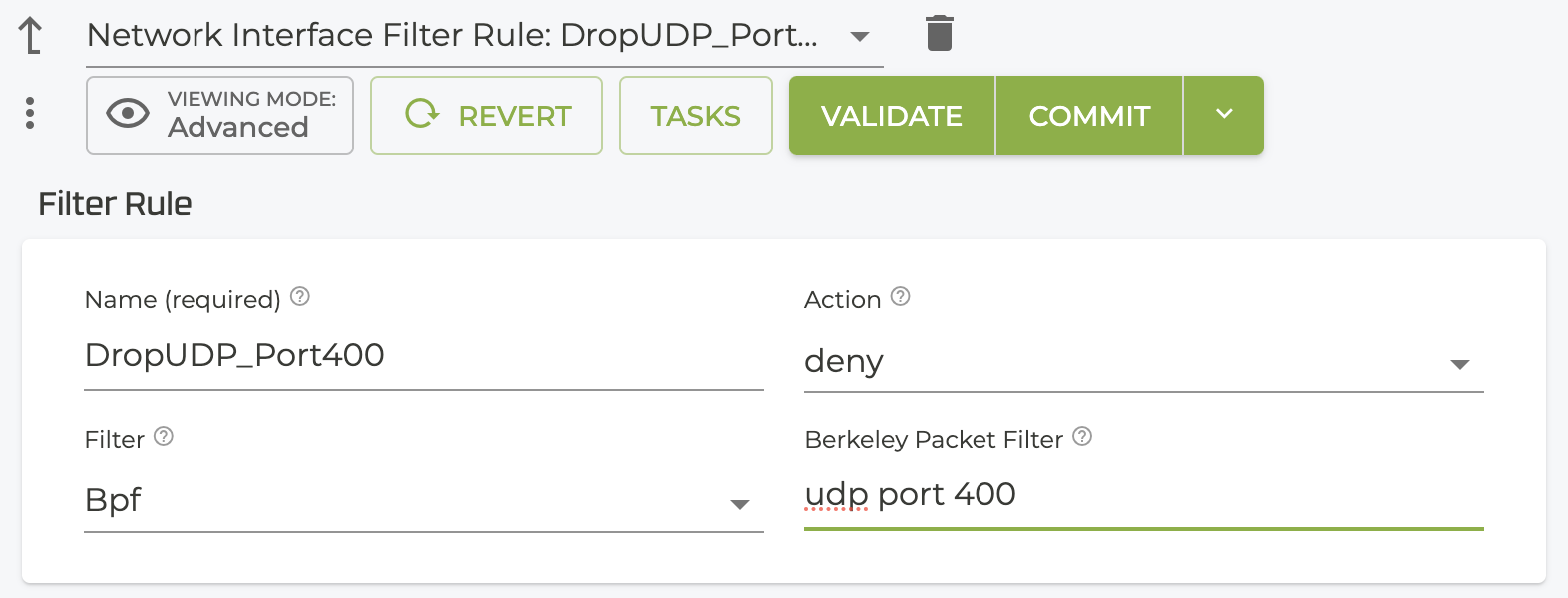
- In the Filter Rule window, define:
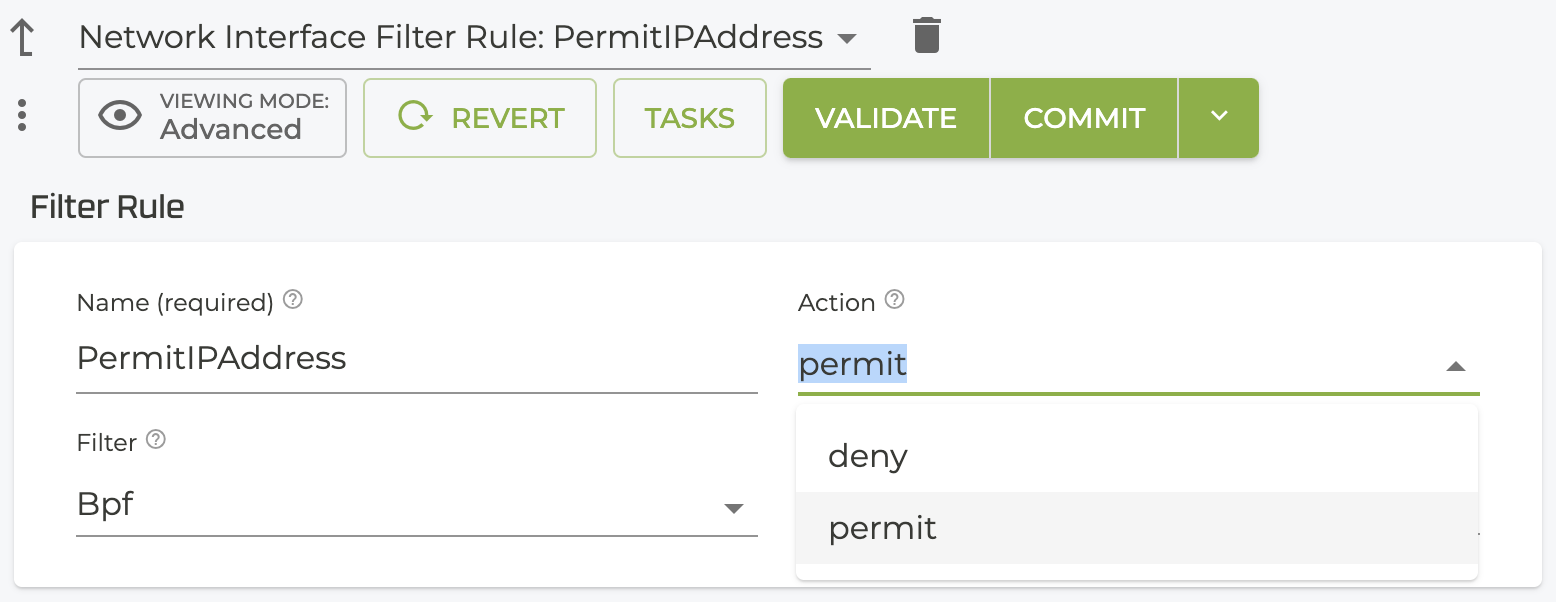
- The Action -
Denydiscards any packets matching the filter applied.Permitallows packets that match the rule to bypass any additional rules, and passes the traffic. - The Filter type - BPF is currently the only option.
- Berkeley Packet Filter - Identifies the filter to be applied. Validation confirms proper BPF syntax.
-
Click Validate and Commit. From the authority drop down, select the network interface to return to the Filter list.
-
Configuration of permit rules follows the same process.
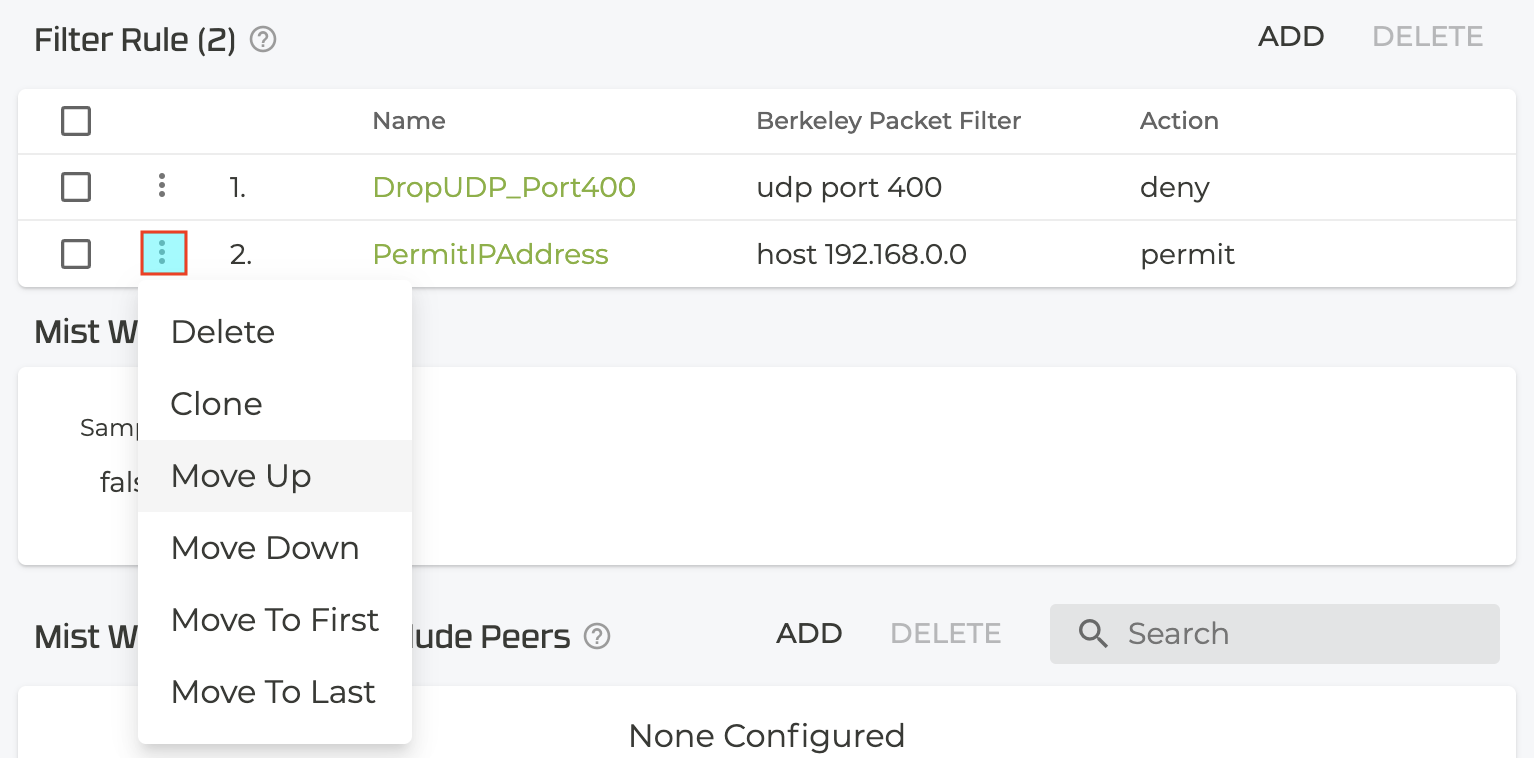
- After the Filter Rule list has been created, you can reorder the rules using the drop down menu to the left of the filter name. This list determines the order in which filter rules are applied.
The number and complexity of rules will have an impact on forwarding performance.
Configure from the PCLI:
*admin@conductor.conductor# configure authority router 128t-west
*admin@conductor.conductor (router[name=128t-west])# node 128t-west
*admin@conductor.conductor (node[name=128t-west])# device-interface bfp-test
*admin@conductor.conductor (device-interface[name=bfp-test])# network-interface intf30
*admin@conductor.conductor (network-interface[name=intf30])# filter-rule DropUDP_Port400
*admin@conductor.conductor (filter-rule[name=DropUDP_Port400])# action deny
*admin@conductor.conductor (filter-rule[name=DropUDP_Port400])# bpf "udp port 400"
*admin@conductor.conductor (filter-rule[name=DropUDP_Port400])# exit
*admin@conductor.conductor (network-interface[name=intf30])# filter-rule PermitIPaddress
*admin@conductor.conductor (filter-rule[name=PermitIPaddress])# action permit
*admin@conductor.conductor (filter-rule[name=PermitIPaddress])# bpf "host 192.168.0.0"
Rules can be moved using the move command:
*admin@conductor.conductor (device-interface[name=bfp-test])# network-interface intf30
*admin@conductor.conductor (network-interface[name=intf30])# move filter-rule DropUDP_Port400 after PermitIPaddress
*admin@conductor.conductor (network-interface[name=intf30])# show
name intf30
filter-rule PermitIPaddress
name PermitIPaddress
bpf "host 192.168.0.0"
action permit
exit
filter-rule DropUDP_Port400
name DropUDP_Port400
bpf "udp port 400"
action deny
exit
Detailed information about Berkeley Packet Filters is outside of the scope of this documentation, but is readily available on the internet.
ICMP
Because ICMP can be an attack vector for a network or used to discover your network topology, ICMP attributes have been updated for firewall protection.
ICMP Type as a Session Attribute
By default, the SSR does not use ICMP codes as a session attribute. However, the SSR does match ICMP error packets with the sessions that generated them, and only accepts those ICMP packets when they match an existing session. For instance, to protect against ICMP attacks from using a barrage of Destination Unreachable messages, if a TCP packet generates a Destination Unreachable, upon receipt of the Destination Unreachable the SSR uses the code to interpret the packet and match it to an existing session. If a match is found, the packet is forwarded to the end host. If a match is not found, the packet is rejected.
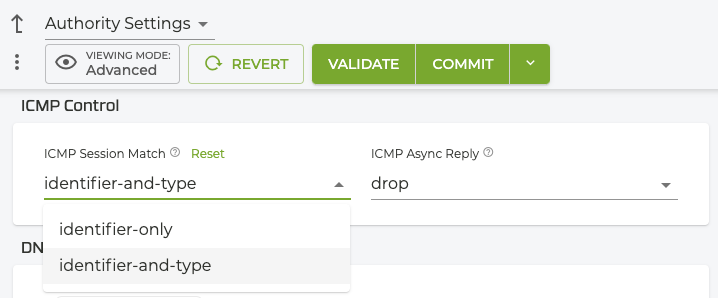
To enable ICMP type as a session attribute:
- At the Authority level, select the Authority Settings button.
- Change the
ICMP Session Matchtoidentifier and type.
Changes take effect after the configuration has been committed.
From the Command Line
*admin@conductor.conductor# configure authority icmp-control icmp-async-reply drop
*admin@conductor.conductor# configure authority icmp-control icmp-session-match identifier-and-type
Discard ICMP Echo Replies With No Request
When you configure the ICMP Async Reply as drop (shown above), any ICMP Echo Replies that arrive at the SSR are dropped if no corresponding request has been seen. This helps to prevent DoS (Denial of Service) attacks such as an ICMP Ping flood.
IPv4 Option Filtering
Attackers sometimes configure IPv4 options incorrectly, producing either incomplete or malformed fields. These malformed packets can be used to compromise hosts on the network. IPv4 Options Filtering provides a mechanism to determine what to do with network data packets based on the options field of the packets. The SSR will inspect the IPv4 header options, compare them to a user defined exclusiont list, and make necessary decisions whether the packets are allowed or dropped and logged.
By default, all IPv4 packets with options are allowed. To configure the dropping of specific IPv4 options, you must first enable drop-all. This reveals the Drop Exclusions list, where you can define IPv4 options to exclude from the drop action.
- At the Authority level, select the Authority Settings button.

- Scroll down to the IPv4 Option Filter button, and select it.

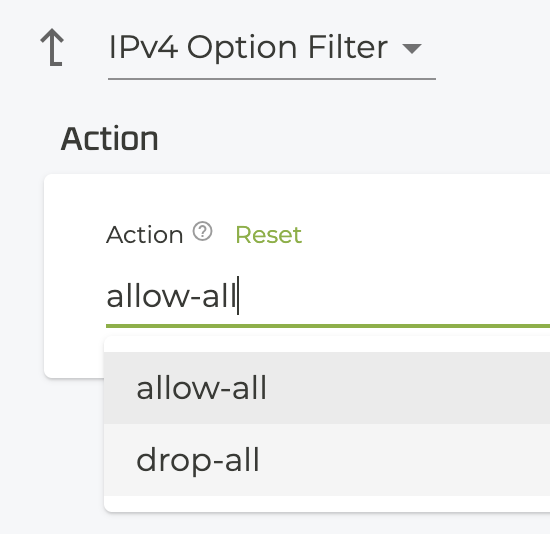
- The IPv4 Options Filter window opens, indicating the
allow-allaction. Open the drop down and selectdrop-all.
If you do not want any allowed options, you can stop here. Return to the Authority level and continue with other configuration activities.
- In the Drop Exclusion field, select ADD.
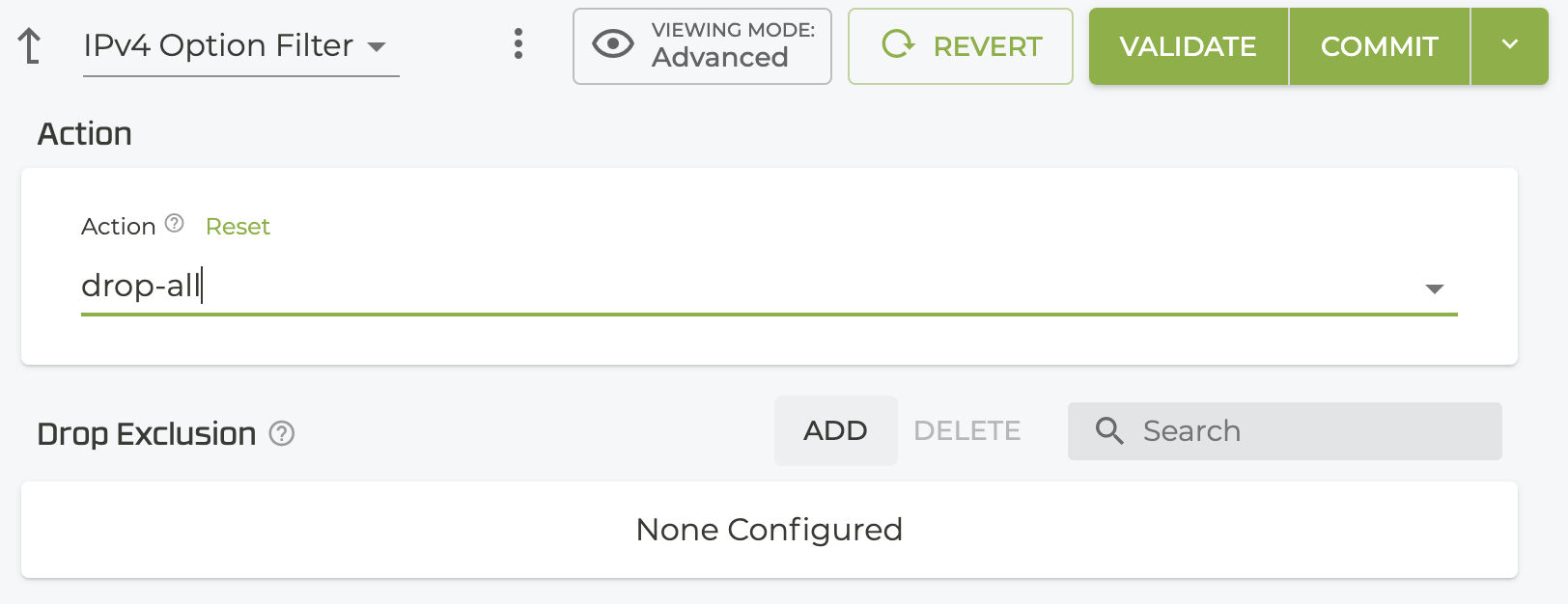
- Enter the Option type/number from the IPv4 Parameters and click Save.
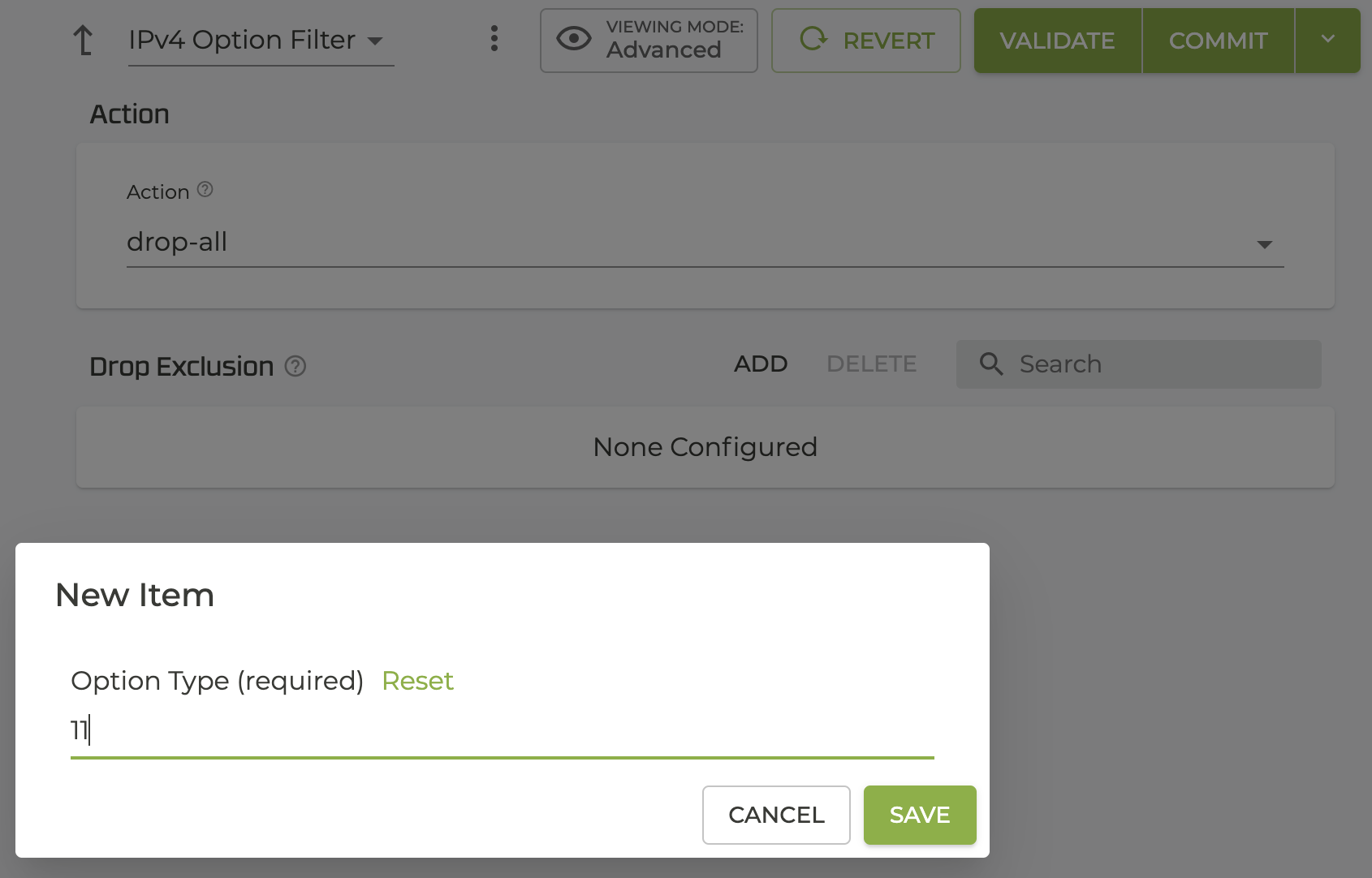
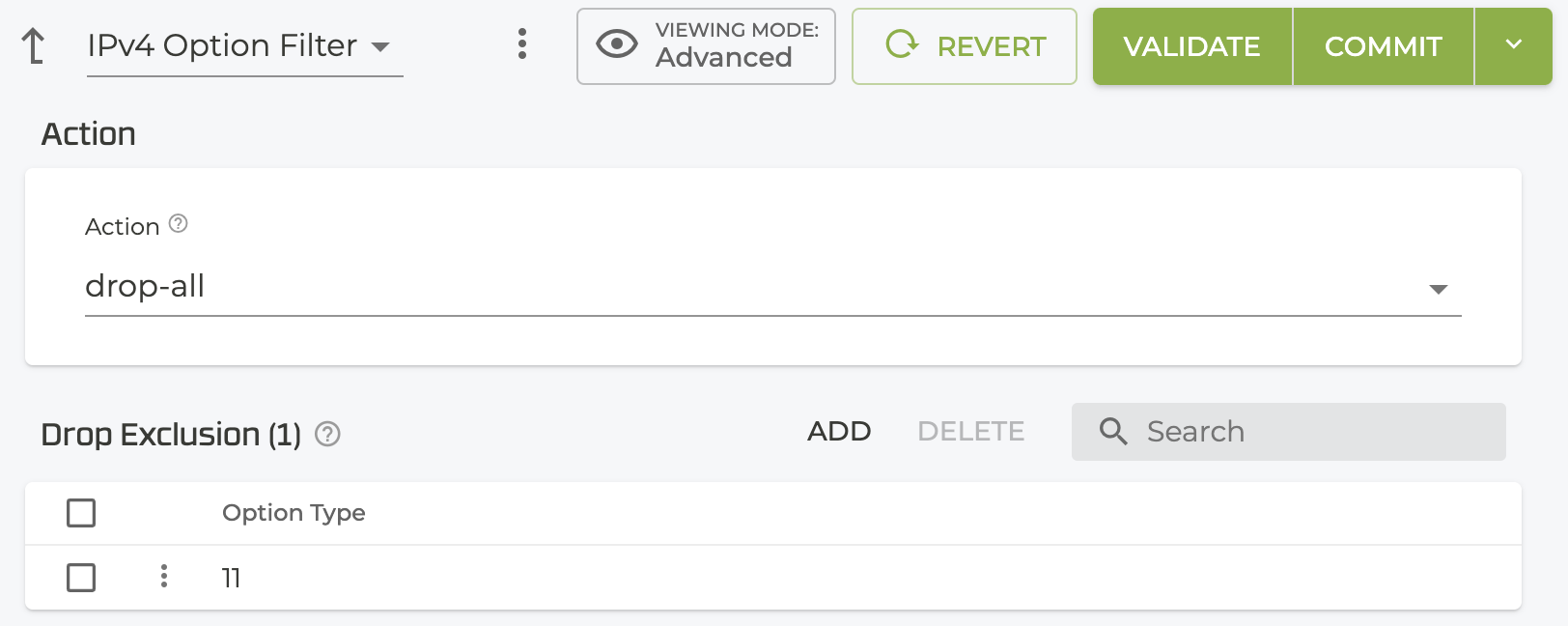
- The new exclusion is listed in the Drop Exclusions table. Click ADD to configure more exclusions.
Using the PCLI
*admin@conductor.conductor# configure authority ipv4-option-filter action drop-all
*admin@conductor.conductor# configure authority ipv4-option-filter drop-exclusion 11
*admin@conductor.conductor# show config candidate authority ipv4-option-filter
config
authority
ipv4-option-filter
action drop-all
drop-exclusion 11
exit
exit
exit
*admin@conductor.conductor#
Broadcast and Multicast Source Addresses
To prevent DoS attacks, packets with broadcast or multicast source IP and MAC addresses are now dropped by default. Otherwise the traffic is propogated across the entire network, flooding the network.
Transport State Enforcement
This functionality sets the action on how the TCP state machine should process unexpected TCP packets. This is important because in some cases where these unexpected packets arrive, it may indicate a TCP Reset attack. By default, the SSR checks and follows the TCP sequence numbers of all the sessions passing through, and increments the associated metrics. Setting the Transport State Enforcement field to Strict ensures any packets in the TCP stream that fall outside of the sequence number stream will be dropped.
- Under Authority, scroll to Service Policies, and select a service policy.
- In the Basic Information panel, click on the Transport State Enforcement drop down and select Strict.
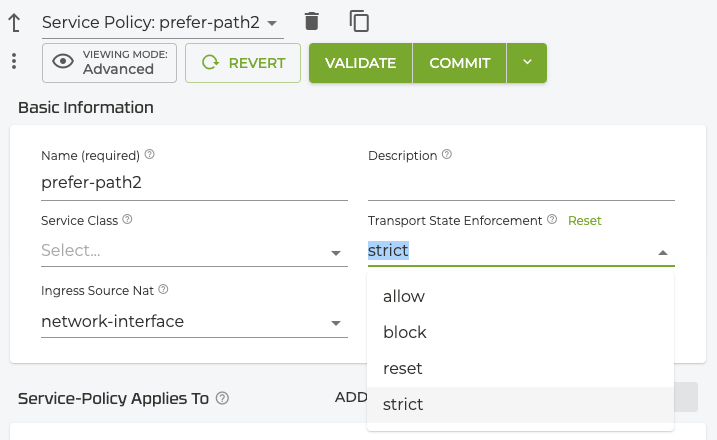
Any packets in the TCP stream that fall outside of the sequence number stream will be dropped. This will apply to any service that has this service policy configured.
From the Command Line
*admin@conductor.conductor# configure authority service-policy prefer-path-2 transport-
state-enforcement strict
*admin@conductor.conductor#
For a detailed description of Transport State Enforcement, refer to Transport State Enforcement. For additional configuration information, see the transport-state-enforcement parameter.
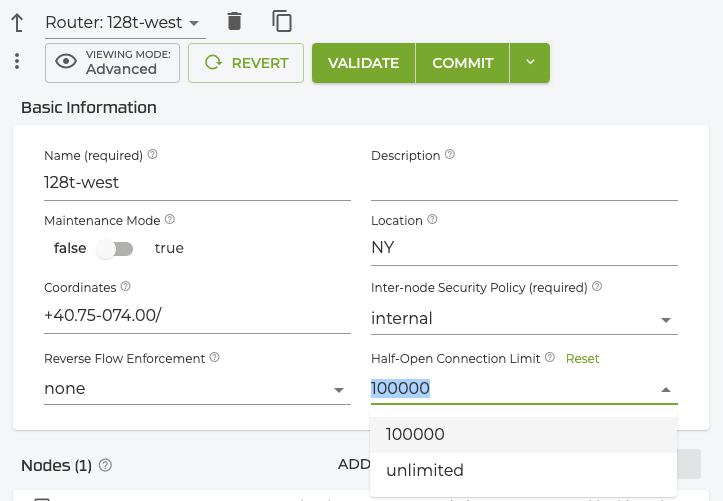
TCP Half-Open Connection Limit
Half-open TCP connections are those where the handshake has started but not completed. An attacker will initiate the handshake in order to take over all available TCP connections, known as a SYN Flood attack or distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack. This prevents service to legitimate traffic and potentially bring down the network.
The SSR provides the ability to configure a limit to these half-open TCP connections.
The connection limit is configured at the router level (Authority > Router), and is unlimited by default. To set a limit, enter a numerical value in the Half-Open Connection Limit field in the Router Basic Information panel. When configured, the SSR tracks how many half-open sessions there are based on existing TCP session state and will deny any new TCP sessions once the limit has been reached.
When the SSR approaches the configured limit of half-open TCP connections, the establishment of healthy TCP sessions may be significantly impacted. Please ensure that this value is set appropriately for your network. More importantly, attempt to identify the devices that are creating half-open sessions.
Additionally, if you require a limit for half-open TCP sessions, it may be helpful to consider the initial TCP session timeout value. The default timer is 10 seconds. If an application fails to establish a TCP socket, the sessions that are in that state will still remain on the SSR for that initial timeout.
An awareness of these two values (half-open limit and TCP session timer) may mitigate the impact of limiting the establishment of healthy TCP sessions.
From the Command Line
*admin@conductor.conductor#
*admin@conductor.conductor# configure authority router 128t-west half-open-connection-l
imit 100000
Correlating Interfaces in Audit Events
To correlate an interface with an audit event, the internal ID of the interface is visible in the show device-interface command.
admin@test1.Fabric128# show device-interface
Fri 2023-10-27 10:06:30 EDT
✔ Retrieving device interface information...
========================================
test1:10
========================================
Type: ethernet
Internal ID: 1
Forwarding: true
PCI Address: 0000:00:04.0
MAC Address: fa:16:3e:88:8d:c1
Admin Status: up
Operational Status: up
Provisional Status: up
Redundancy Status: non-redundant
Speed: 10 Gb/s
Duplex: full
in-octets: 360
in-unicast-pkts: 4
in-errors: 0
out-octets: 0
out-unicast-pkts: 0
out-errors: 0
Plugin Info: unavailable
Use this information to match an interface ID for an audit log using the show events command.
==================================================================
2023-10-27T02:56:51.513Z Traffic request violates access policy.
==================================================================
Type: traffic.denied
Node: test1
Denied Reason: access
Destination Address:172.16.2.201
Destination Port: 443
Ingress Interface: 1.0
Ip Protocol: udp
Permitted: False
Source Address: 172.16.1.201
Source Port: 10000