LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network.1 The SSR Networking Platform can be configured to leverage an LDAP server to authenticate administrative users to the PCLI and GUI interfaces for administration, configuration, and management.
Basic Configuration
Configuring LDAP on the SSR is done globally, and is done within the authority > ldap-server configuration element. The SSR authority configuration may only have one ldap-server configured at a time.
The ldap-server configuration has the following attributes:
- name: a unique name that the SSR uses to reference this configuration.
- address: the IP address or FQDN of the LDAP server.
If using an FQDN/hostname, this name must be resolvable by the SSR.
- search-base: The search base defines the starting point for the search in the directory tree. For example, SSR might need to query the entire directory, in which case the search base must specify the root of the directory service. Or, SSR might need to query a specific organizational unit (OU) in the directory. Generally this is configured as a series of Domain Components, which are abbreviated "dc."
- server-type: An enumeration, which can be global-catalog, ldaps, or starttls. For Active Directory LDAP servers, use
global-catalog. LDAPS is LDAP wrapped in SSL, and is a non-standard (yet popular) implementation. StartTLS is instead built into the LDAP protocol itself. Consult your LDAP server's documentation to determine the server-type most appropriate for your deployment.
The default type is ldaps, which requires TLS/SSL for the entire duration of the connection
The "starttls" type will not send user passwords in the process of being validated in the clear (it requires that STARTTLS be performed, and uses that channel for sending the password), but all other LDAP traffic (including the bind request and credentials used for binding) are sent in the clear.
- port: the listening port on your LDAP server. Using
server-type-defaultwill select the default port based on the server-type configured (3269 for global-catalog, 636 for LDAPS, 389 for StartTLS) - bind-type: an enumeration of anonymous, unauthenticated, or password. This is how your SSR will authenticate to your LDAP server.
- distinguished-name: the name to use when binding to the server; available when bind-type is set to
password. - password: the password to use to bind to the server (available when bind-type is set to
password)
The following ldap-server configuration options have been added with SSR Version 5.5.2:
- certificate-assurance: Allows the SSR to perform different levels of server certificate verification in a TLS session. The following values can be specified:
- Weak: Do not request or check any server certificates.
- Mild: Ignore invalid or missing certificates, but check for hostname.
- Moderate: Terminate on invalid certificate, but ignore missing certificates.
- Strong: (Default) Terminate on invalid and missing certificates.
- auto-generate-filter: Turn on or off user- and group-based filters automatically.
- True: (Default) SSR generates user- and group-based filters.
- False: SSR does not generate user- and group-based filters.
- user-search-base: Allows users to set user-search-base filters when auto-generate-filter is false for server-type global-catalog. See the configuration examples below for usage.
- group-search-base: Allows users to set group-search-base filters when auto-generate-filter is false for server-type global-catalog. See the configuration examples below for usage.
LDAP Server Configuration
The following section provides example configuration steps for an LDAP server.
LDAP Server on JumpCloud
JumpCloud is a cloud based identity provider that supports centralized user management using LDAP and is used as an example of how to configure an LDAP Server.
JumpCloud is not affiliated with Juniper, and Juniper does not endorse the use of JumpCloud. It is used here only as an example of one way to configure an LDAP server.
Set up LDAP bind user in the JumpCloud portal
- Create a user with access to search the LDAP directory. Make a note of the password and LDAP distinguished name strings for this user. You will need to add this to the SSR Conductor LDAP config.
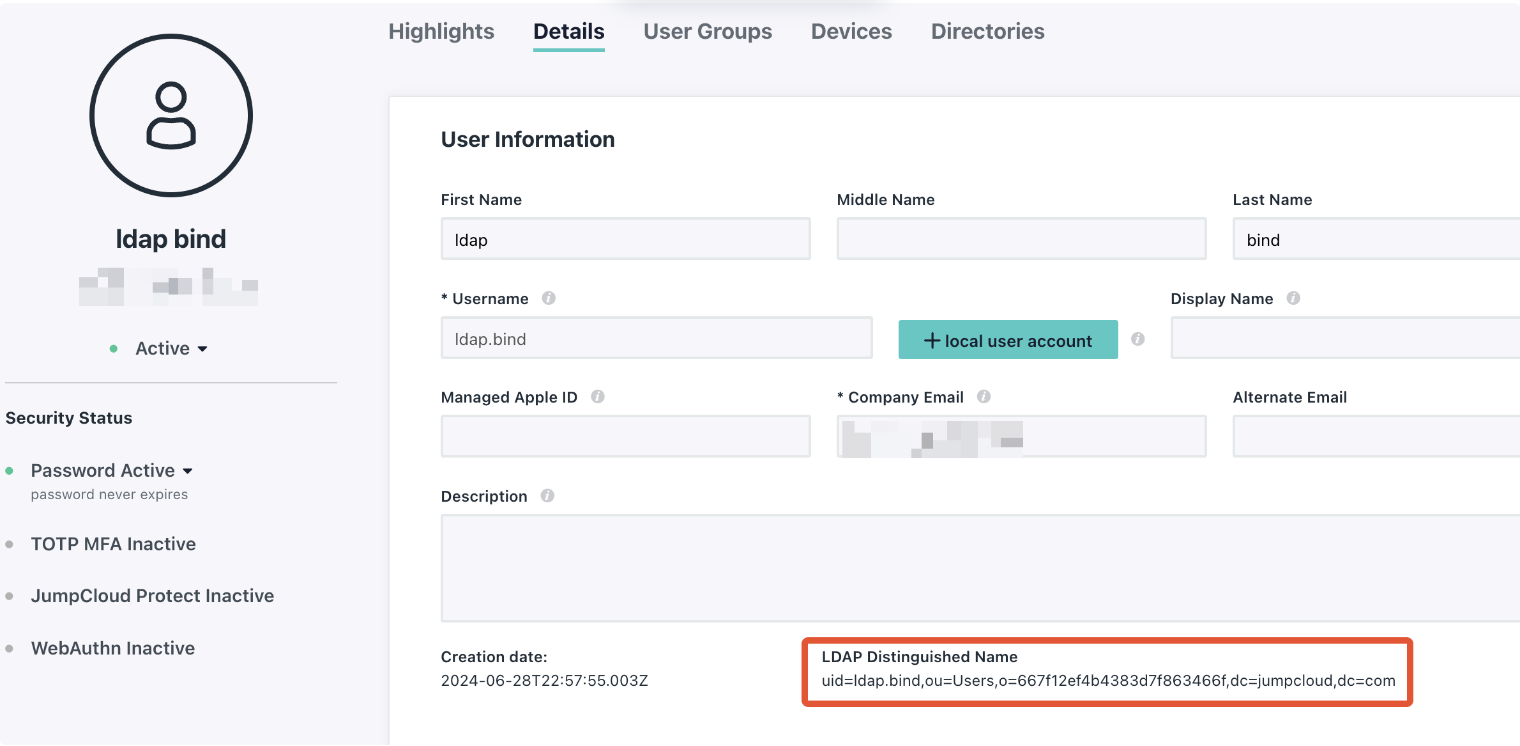
- Ensure the LDAP user has permissions to search and bind the LDAP server.
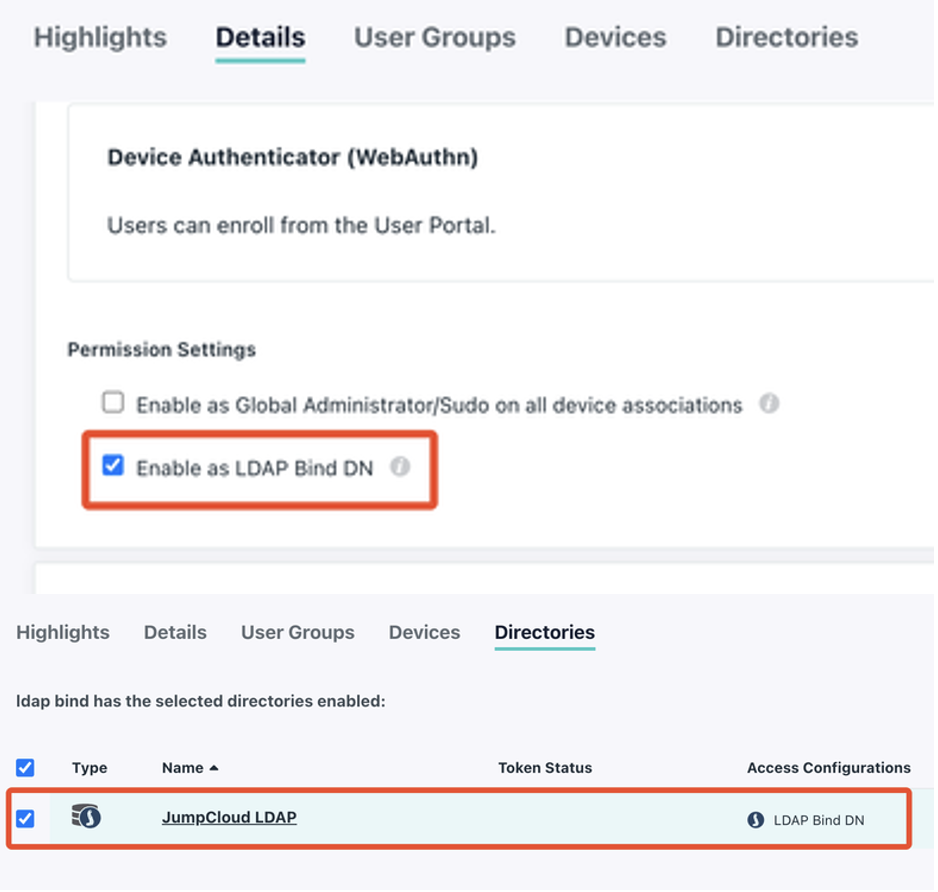
- Under the Details tab, set Permission Settings to
Enable as LDAP Bind DN. - Under the Directories tab, select the
JumpCloud LDAPdirectory.
Set up groups in the JumpCloud portal
- Create
128t-adminand128t-usergroups in the JumpCloud portal.
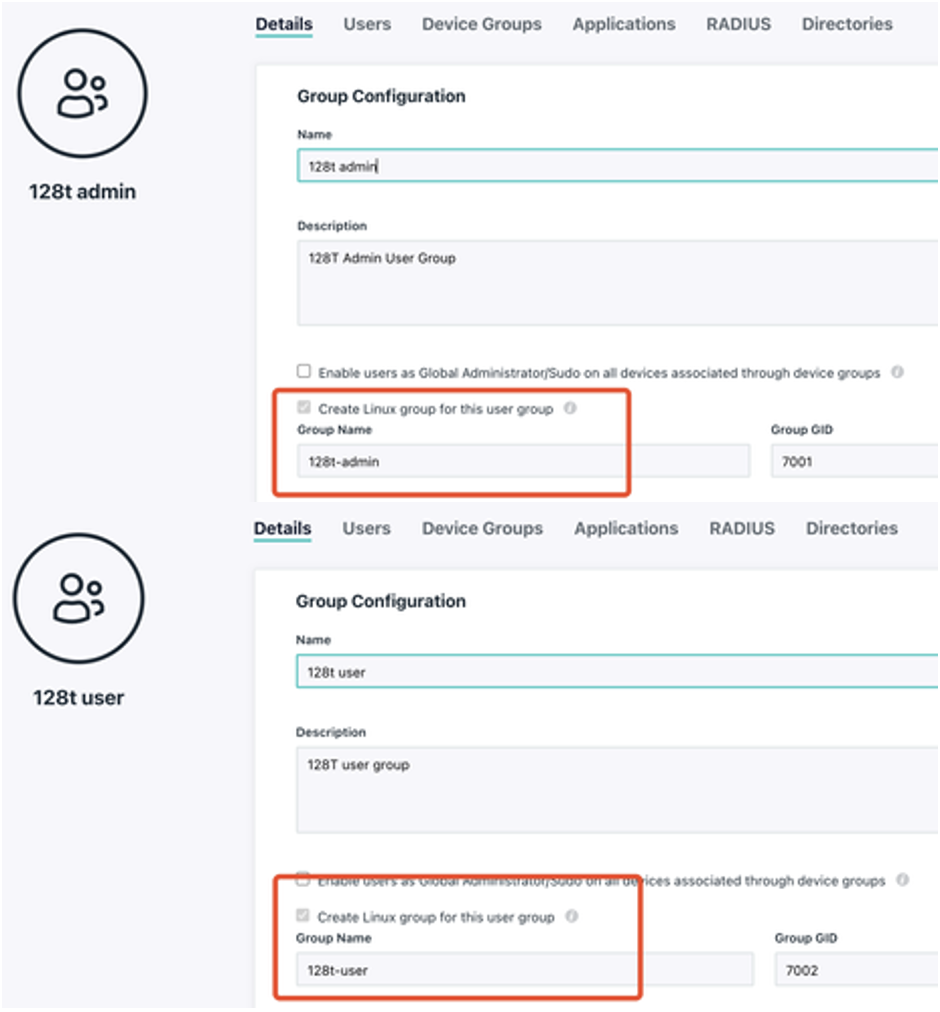
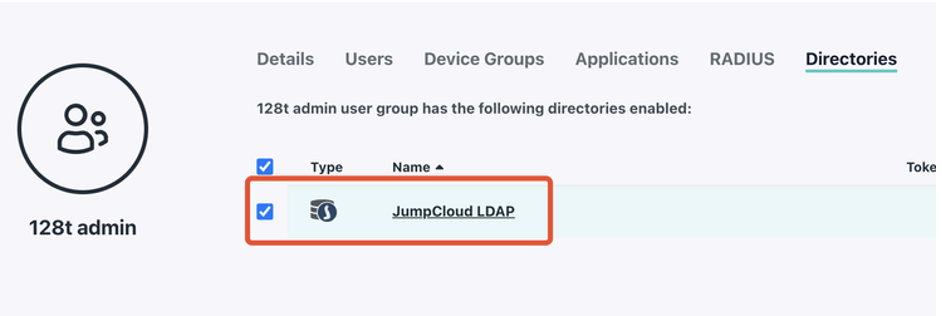
- For the
128t-adminand128t-usergroup, ensure each are enabled for the LDAP server in the Directories menu.
Add users to groups in the JumpCloud portal
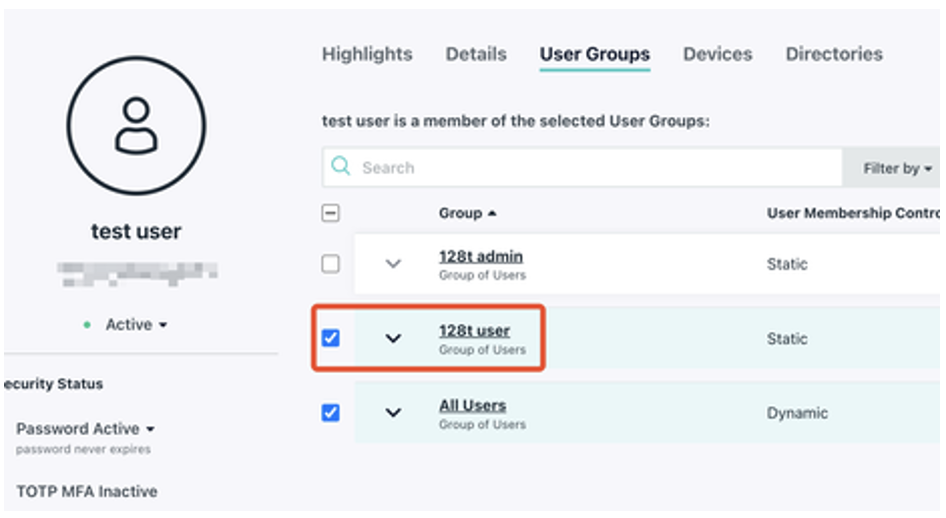
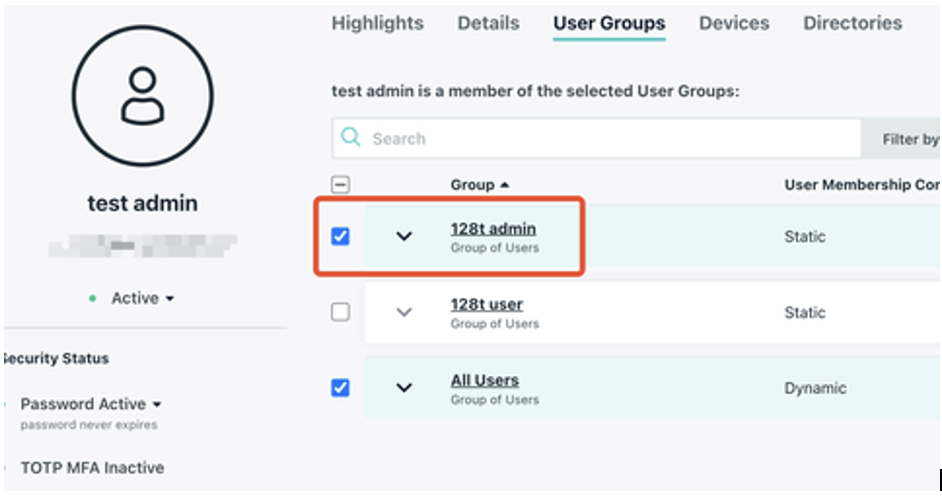
Select users and assign them to either the 128t-user or 128t-admin groups.
JumpCloud Configuration on the SSR
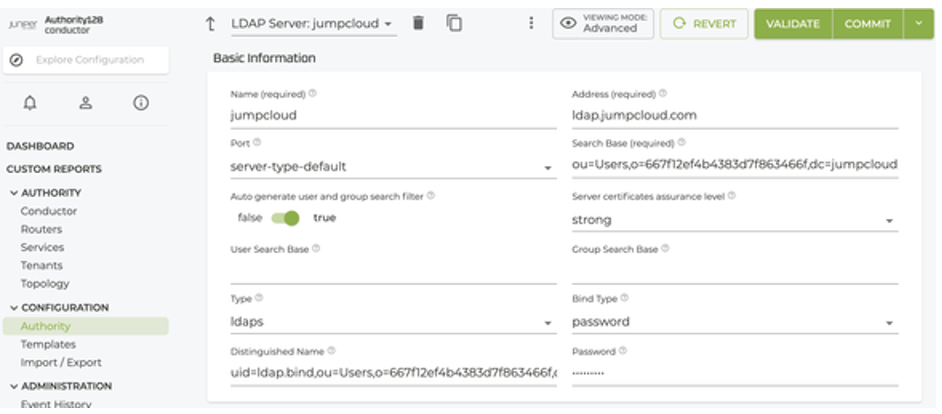
On the SSR conductor, configure the JumpCloud LDAP server.
Use the LDAP bind user distinguished name and password from the first step for these server settings. Change the search-base and distinguished-name strings based on your JumpCloud settings.
Example - CLI
ldap-server jumpcloud
name jumpcloud
address ldap.jumpcloud.com
search-base ou=Users,o=667f12ef4b4383d7f863466f,dc=jumpcloud,dc=com
certificate-assurance strong
server-type ldaps
bind-type password
distinguished-name uid=ldap.bind,ou=Users,o=667f12ef4b4383d7f863466f,dc=jumpcloud,dc=com
password (removed)
exit
Example - GUI
User Verification
Do NOT manually create local user accounts for LDAP users. They are automatically added based on the details for each user returned from the LDAP server. Manually creating local users prevents the use of the LDAP server for authentication.
The first time a user successfully logs in to the Conductor or Router (using either the CLI or the GUI) the SSR reaches out to the JumpCloud LDAP server and configures the user environment. Below is an example CLI login output of an LDAP authenticated user:
~ % ssh test.user@172.25.128.234
test.user@172.25.128.234's password:
First time login, configuring...
Creating home directory for test.user.Reloading audit rules
No rules
No rules
enabled 1
failure 1
pid 18750
rate_limit 0
backlog_limit 8192
lost 0
backlog 0
enabled 1
failure 1
pid 18750
rate_limit 0
backlog_limit 8192
lost 0
backlog 4
+---------------------------------------+
| |
| Welcome to: |
| |
| | . . ,---. . ,---. ,---. ,--. |
| | | | | | | |---' |---' | |
| | `---' ' ' ' ' `---' ' |
| ---' |
| __ ___ __ __ __ |
| |\ | |_ | | | / \ |__) |_/ (_ |
| | \| |__ | |/\| \__/ | \ | \ __) |
| |
| Session Smart Networking Platform ... |
+---------------------------------------+
test.user@node0.r1>
test.user@node0.r1>
test.user@node0.r1> quit
Connection to 172.25.128.234 closed.
Additionally, to verify the status of your configured users and the LDAP server, click on Users in the Adminstration menu on the left side of the SSR GUI. LDAP authenticated users appear in the users list after they have successfully logged in. From the CLI, use the show users command.
Important Clarification
As a point of clarification: The New User button in the top right corner of the GUI is intended for use cases such as RADIUS or local users and is not to be configured for LDAP. Using the new user button to manually create a local user prevents the use of the LDAP server for authentication.
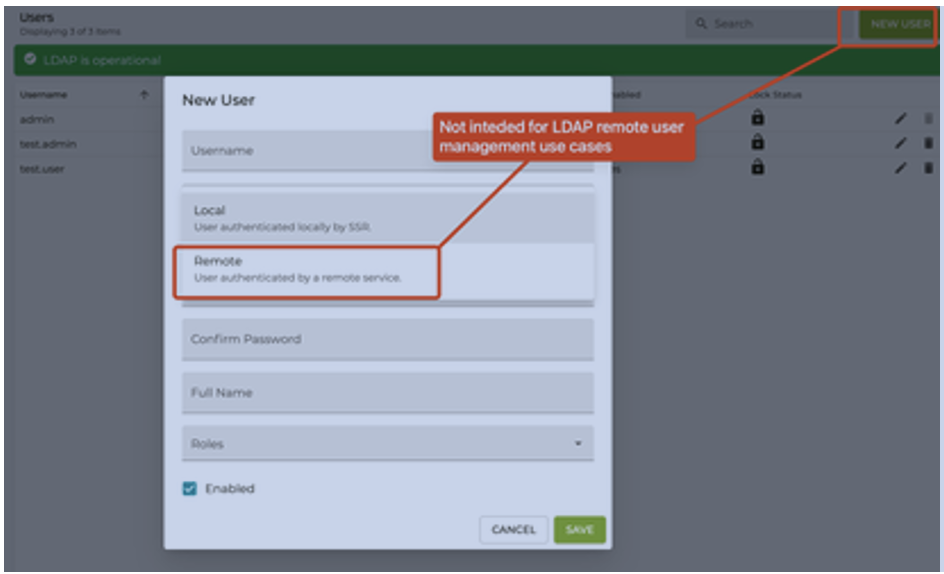
In the case of LDAP, both the user and the authentication are administered remotely.
Microsoft Active Directory Sample Configurations
The following sample configuration interfaces with Microsoft Active Directory.
ldap-server ActiveDirectory
name ActiveDirectory
address activedirectory.mydomain.com
search-base DC=mydomain,DC=com
server-type global-catalog
port server-type-default
bind-type password
distinguished-name "CN=commonname,OU=orgunit,DC=mydomain,DC=com"
password (removed)
exit
certificate-assurance Configuration Example
admin@test1.RTR_EAST_CONDUCTOR (ldap-server[name=myldap])# show
name myldap
address ad.systemsadtest.local
search-base dc=systemsadtest,dc=local
auto-generate-filter true
certificate-assurance strong
server-type global-catalog
port server-type-default
bind-type password
distinguished-name ldapuser@systemsadtest.local
password (removed)
auto-generate-filter Configuration Example
admin@test1.RTR_EAST_CONDUCTOR (ldap-server[name=myldap])# show
name myldap
address ad.systemsadtest.local
search-base dc=systemsadtest,dc=local
auto-generate-filter false
certificate-assurance strong
server-type global-catalog
port server-type-default
bind-type password
distinguished-name ldapuser@systemsadtest.local
password (removed)
user-search-base and group-search-base Configuration Examples
admin@test1.RTR_EAST_CONDUCTOR (ldap-server[name=myldap])# show
name myldap
address ad.systemsadtest.local
search-base dc=systemsadtest,dc=local
auto-generate-filter false
certificate-assurance strong
user-search-base DC=DIR, DC=slb,DC=com?subtree?(|(&(objectCategory=user)(memberOf=CN=128t-admin,OU=EAR-AA-899,OU=Applications,OU=Groups,DC=DIR,DC=slb,DC=com)))
group-search-base OU=EAR-AA-899,OU=Applications,OU=Groups,DC=DIR,DC=slb,DC=com?subtree?(&(objectclass=group)(|(cn=128t-admin)(cn=128t-user)))
server-type global-catalog
port server-type-default
bind-type password
distinguished-name ldapuser@systemsadtest.local
password (removed)
LDAP User Account Requirements
It is important to ensure that administrative users are configured on the LDAP server as being a member of a group called 128t-user for read-only access to the configuration, or 128t-admin for read-write access to configuration. These group names are case sensitive.
Implementation Notes
show userwithin the PCLI (and GUI's User management page) allows viewing LDAP users that have connected to SSRedit userwithin the PCLI (and GUI's User management page) allows editing LDAP users, (changing password, display name, enabled/disabled). While saving these changes may report back that it has completed successfully, these changes are not saved in the LDAP server.- Having local SSR users with the same name as LDAP users is not supported.
- The "admin" user is always authenticated locally; any "admin" user in ldap is ignored
- If the TLS certificates for LDAP servers are not from a CA recognized by openssl's CA bundle, trust for the certificate must be configured manually (in linux)
- When the system is configured to use LDAP for user authentication, the status of the LDAP connection can be seen on the Users page of the GUI. This is a high level status of connectivity to retrieve user and group information based on the LDAP configuration.
Logging
The LDAP log category allows you to change the LDAP log level.
admin@test1.RTR_EAST_CONDUCTOR# set log level category ldap
configured debug error fatal force info node router trace warning
admin@test1.RTR_EAST_CONDUCTOR# set log level category ldap debug
✔ Setting log level...
Log level successfully set
Debugging Issues Using LDAP
For diagnosing connection status from linux
sssctl domain-status <name-of-configured-ldap-server-in-128t-config>
To test what a user's current group memberships are from linux
id -Gn <user-name>
There is a minimum delay of 5 minutes from when a user's groups are retrieved before the server will be consulted again, so changes that are made on the server may appear to lag a bit.
sss_cache -u <user>