Configuring Service and Topology Exchange Protocol (STEP)
Use the information in this section to enable routers to connect to the STEP repository on the conductor and build their STEP documents. Additionally, information about configuring reporting parameters, and using the show commands to view STEP details is provided.
Enable STEP
The STEP repository is located on the Conductor, and the repository process runs by default. Use the step-repo command to assign the IP Address for the repository on the conductor. The routers use this address to connect to the repository and build the STEP document.
Use the following command to enable the STEP repository on the Conductor.
config authority
step-repo 11.1.1.1
address 11.1.1.1
description "STEP Repository on the Conductor"
exit
When STEP is enabled on an existing router, it is a best practice to clear all existing sessions so the routers begin using the STEP-based routes. This is especially important for EoSVR configurations, to prevent stuck flows and traffic from being dropped. Use the command delete sessions service <service-name> or delete sessions service <eosvr-service-name> to clear sessions.
When configuring STEP repositories for high availability, the above configuration must be created on both repositories. See STEP Repository High Availability for more information.
Configuring Peer Path Advertisement Settings
The weighted moving average and reporting delay parameters can be configured per neighborhood:
config
authority
router NorthEast
node node1
device-interface wan3
network-interface wan3
neighborhood broadband
step-peer-path-advertisement
sla-metrics
moving-average-sample-size 3
significance-threshold
min-loss 0.1
min-latency 5
min-jitter 2
exit
increase-report-delay 1
percentage 1
delay 1800
exit
increase-report-delay 10
percentage 10
delay 240
exit
increase-report-delay 20
percentage 20
delay 150
exit
increase-report-delay 50
percentage 50
delay 30
exit
increase-report-delay 100
percentage 100
delay 15
exit
increase-report-delay 200
percentage 200
delay 1
exit
decrease-report-delay 1
percentage 1
delay 1800
exit
decrease-report-delay 10
percentage 10
delay 240
exit
decrease-report-delay 50
percentage 50
delay 15
exit
Any auto-generated adjacency in the neighborhood reflects the same configuration values:
config
authority
router NorthEast
node node1
device-interface wan3
network-interface wan3
adjacency 10.0.3.23 West
step-peer-path-advertisement
sla-metrics
moving-average-sample-size 3
significance-threshold
min-loss 0.1
min-latency 5
min-jitter 2
exit
increase-report-delay 1
percentage 1
delay 1800
exit
increase-report-delay 10
percentage 10
delay 240
exit
increase-report-delay 20
percentage 20
delay 150
exit
increase-report-delay 50
percentage 50
delay 30
exit
increase-report-delay 100
percentage 100
delay 15
exit
increase-report-delay 200
percentage 200
delay 1
exit
decrease-report-delay 1
percentage 1
delay 1800
exit
decrease-report-delay 10
percentage 10
delay 240
exit
decrease-report-delay 50
percentage 50
delay 15
exit
Note that the effective values are those in the adjacency. The adjacency configuration may be auto-generated or manually configured. The values configured in the neighborhood have no direct effect on the router behavior, they only provide the input for instantiating adjacency objects.
If moving-average-sample-size or significance-threshold is not configured, the default values will be used. Likewise, if increase-report-delay or decrease-report-delay is not configured, the default configuration is in effect.
Router District Settings
The rate limit parameters for peer path SLA updates to the STEP router document can be configured for each router from within the default-district parameters:
config
authority
router NorthEast
district-settings default-district
district-name default-district
step-peer-path-sla-metrics-advertisement
update-rate-limit 180
minimum-update-interval 30
update-burst-size 2
exit
exit
Only the default district parameters have any effect. If no district-settings are configured, or if any of the step-peer-path-advertisement values are not provided, the default values will be used.
Hierarchical Services
It is possible to configure a child service that is only visible to a subset of routers in the authority. A router configured with the child service (and a local service-route that applies to it) may advertise the availability of this child service in its STEP router document.
A router without the child service visible in its configuration will calculate a STEP route for the service, but only if the parent service is available. The route calculation for the child service is based on the parent’s service-policy. The resulting STEP route is visible via the show step route command, but it is not used for forwarding because it is not installed in the FIB and load-balancer.
Instead, the transit router forwards based on the parent’s service-paths. This only works when the access tenant for the child service is also allowed in the parent’s service configuration.
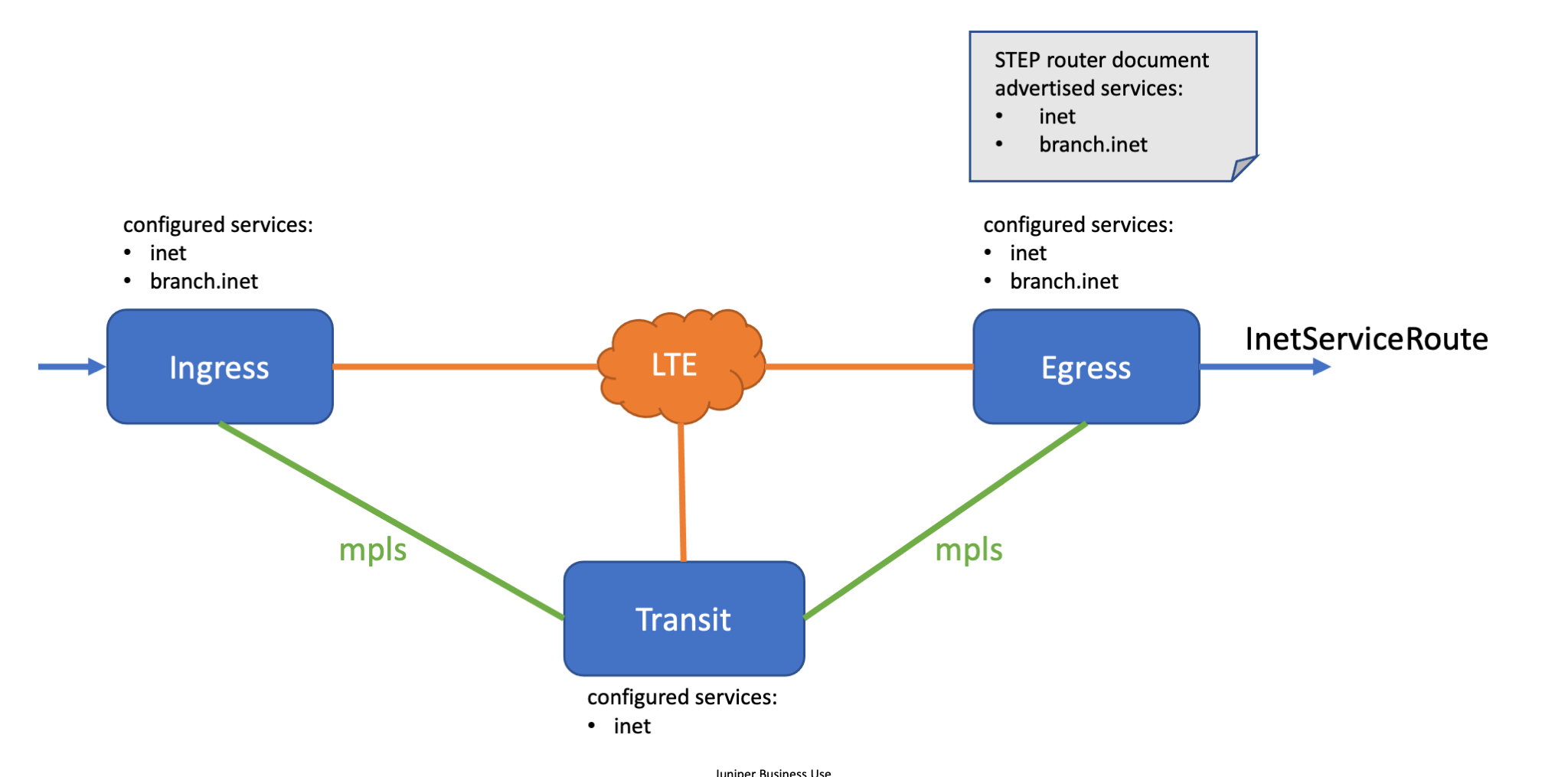
Example
config
authority
router Ingress
router-group BranchRouters
exit
router Egress
router-group BranchRouters
service-route InetServiceRoute
service-name inet
next-hop combo-west intf11
vector net2
exit
exit
exit
router Transit
exit
service inet
scope private
transport udp
port-range 443
start-port 443
exit
exit
address 0.0.0.0/0
access-policy red
permission allow
exit
service-policy InetServicePolicy
exit
service branch.inet
applies-to router-group
group-name BranchRouters
exit
address 172.16.2.201
exit
service-policy InetServicePolicy
vector mpls
priority 100
exit
vector lte
priority 500
exit
vector net2
priority 7
exit
session-resiliency revertible-failover
exit
exit
exit
The transit router has a STEP route for the child service branch.inet but forwarding is performed based on the parent service inet:
admin@conductor-node-1.Conductor# show step routes router Transit
============= ============= =================
Node Name Service IP Prefix
============= ============= =================
transit branch.inet 172.16.2.201/32
transit inet 0.0.0.0/0
admin@conductor-node-1.Conductor# show service-path router Transit node transit
========= ================================ ====== =============== ============ =========== ======== ====== ====== ============= ========
Service Service-Route Type Destination Next-Hop Interface Vector Cost Rate Capacity State
========= ================================ ====== =============== ============ =========== ======== ====== ====== ============= ========
inet __inet_0.0.0.0/0_Egress:egress step 172.16.3.3/32 172.16.3.3 intf10 lte 500 0 0/unlimited Up(Up)
inet __inet_0.0.0.0/0_Egress:egress step 172.16.4.3/32 172.16.4.3 intf12 mpls 100 0 0/unlimited Up(Up)
The ingress router has both a STEP route, and service-paths for the child service branch.inet:
admin@conductor-node-1.Conductor# show step routes router Ingress
============ ============= =================
Node Name Service IP Prefix
============ ============= =================
ingress branch.inet 172.16.2.201/32
ingress inet 0.0.0.0/0
admin@conductor-node-1.Conductor# show fib router Ingress hierarchy-service-name inet
==================== ====== ======= ======== ===== ============= ============ ======== ======
IP Prefix Port Proto Tenant VRF Service Next Hops Vector Cost
==================== ====== ======= ======== ===== ============= ============ ======== ======
0.0.0.0/0 443 UDP red - inet 172.16.4.4 mpls 100
172.16.3.3 lte 500
172.16.2.201/32 443 UDP red - branch.inet 172.16.4.4 mpls 100
172.16.3.3 lte 500
admin@conductor-node-1.Conductor# show service-path router Ingress node ingress
============= ============================================= ====== =============== ============ =========== ======== ====== ====== ============= ========
Service Service-Route Type Destination Next-Hop Interface Vector Cost Rate Capacity State
============= ============================================= ====== =============== ============ =========== ======== ====== ====== ============= ========
branch.inet __branch.inet_172.16.2.201/32_Egress:egress step 172.16.3.3/32 172.16.3.3 intf11 lte 500 0 0/unlimited Up(Up)
branch.inet __branch.inet_172.16.2.201/32_Egress:egress step 172.16.4.4/32 172.16.4.4 intf12 mpls 100 0 0/unlimited Up(Up)
inet __inet_0.0.0.0/0_Egress:egress step 172.16.3.3/32 172.16.3.3 intf11 lte 500 0 0/unlimited Up(Up)
inet __inet_0.0.0.0/0_Egress:egress step 172.16.4.4/32 172.16.4.4 intf12 mpls 100 0 0/unlimited Up(Up)
Route Computation
When STEP determines the best route to use, it takes the following information from the service-policy into consideration.
-
Best Path Selection Criteria in the
service-policyselection options are now considered: vector and average-latency. MOS is not supported for STEP route computation. In releases prior to 5.6, STEP assumed thevectorvalue. -
Path Quality Measure is considered during the STEP route computation when Service Level Agreement is enabled in the
service-policy(Path Quality Filter is set totrue). Peer-paths that do not meet the SLA are penalized during the route computation. When the Use Best-Effort Paths is set tofalse, those peer-paths are not used at all.
Configurable Parameters
See step-peer-path-advertisement (adjacency) for configuration details.
step peer path advertisement
sla-metrics
moving average sample size
significance threshold
min-loss
min-latency
min-jitter
increase report delay
percentage
delay
decrease-report-delay
percentage
delay
See step-peer-path-advertisement (district) for configuration details.
district-settings
default-district
district-name
step-peer-path-sla-metrics-advertisement
update-rate-limit
minimum-update-interval
update-burst-size